Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including energy production, nerve function, and bone health. One of the most common forms of magnesium is the magnesium ion, which is a positively charged particle that forms when magnesium atoms lose or gain electrons. But what charge does a magnesium ion form?
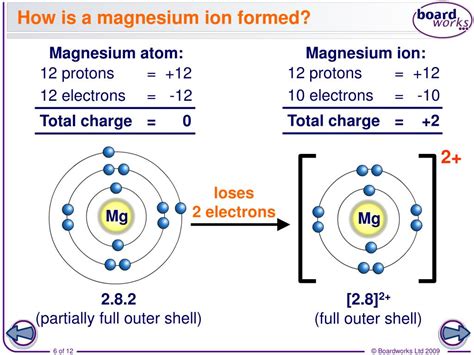
Magnesium ions are formed when magnesium atoms undergo a process called ionization, where they lose or gain electrons to achieve a more stable electronic configuration. In the case of magnesium, the ionization process involves the loss of two electrons from the outermost energy level of the atom. This results in the formation of a positively charged ion, known as a cation.
Understanding Ionization

Ionization is a fundamental process in chemistry that involves the gain or loss of electrons by atoms or molecules. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it forms a positively charged ion, known as a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains one or more electrons, it forms a negatively charged ion, known as an anion.
In the case of magnesium, the ionization process involves the loss of two electrons from the outermost energy level of the atom. This results in the formation of a positively charged ion, known as Mg2+, which has a +2 charge.
Formation of Magnesium Ions
The formation of magnesium ions involves the loss of two electrons from the outermost energy level of the atom. This process can be represented by the following equation:
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e-
In this equation, the magnesium atom (Mg) loses two electrons (2e-) to form a positively charged ion (Mg2+).
Charge of Magnesium Ions

As mentioned earlier, magnesium ions have a +2 charge, which is denoted by the symbol Mg2+. This means that the magnesium ion has two positive charges, which makes it a strong electropositive ion.
The +2 charge of magnesium ions is due to the loss of two electrons from the outermost energy level of the atom. This loss of electrons results in a net positive charge, which is characteristic of cations.
Importance of Magnesium Ions
Magnesium ions play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including energy production, nerve function, and bone health. They are also involved in many industrial applications, such as the manufacture of fireworks, flares, and sparklers.
In the human body, magnesium ions are involved in many biochemical reactions, including the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency of the body. They also play a crucial role in nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone mineralization.
Biological Functions of Magnesium Ions

Magnesium ions are involved in many biological functions, including:
- Energy production: Magnesium ions play a crucial role in the production of ATP, which is the primary energy currency of the body.
- Nerve function: Magnesium ions are involved in the transmission of nerve impulses, which is essential for communication between nerve cells.
- Muscle contraction: Magnesium ions are involved in muscle contraction and relaxation, which is essential for movement and locomotion.
- Bone mineralization: Magnesium ions are involved in the mineralization of bones, which is essential for bone health and development.
In conclusion, magnesium ions are positively charged particles that form when magnesium atoms lose or gain electrons. They have a +2 charge, which is denoted by the symbol Mg2+. Magnesium ions play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including energy production, nerve function, and bone health.
What is the charge of a magnesium ion?
+The charge of a magnesium ion is +2.
What is the symbol for a magnesium ion?
+The symbol for a magnesium ion is Mg2+.
What is the importance of magnesium ions in the human body?
+Magnesium ions are involved in many biological functions, including energy production, nerve function, and bone health.