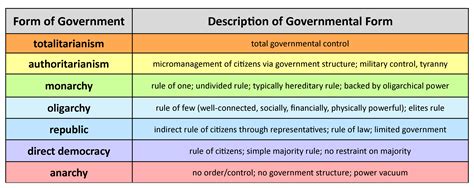
In the realm of governance, the concept of a republic form of government has been a cornerstone of democracy for centuries. The term "republic" is often used interchangeably with "democracy," but it holds distinct characteristics that differentiate it from other forms of governance. At its core, a republic is a system of government where the people elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. However, this simplistic definition does not fully capture the essence of a republic. In this article, we will delve into the five key features that define a republic form of government, exploring its significance, benefits, and implications for citizens and governance.
Representative Democracy

One of the fundamental features of a republic is its reliance on representative democracy. In a republic, citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. This contrasts with direct democracy, where citizens vote directly on laws and policies. Representative democracy allows for more efficient decision-making, as elected officials are tasked with studying and debating issues in-depth. However, this system also relies on the trust and accountability of the representatives, who must act in the best interests of their constituents.
The Role of Elected Representatives
In a republic, elected representatives are expected to serve as the voice of the people. They are responsible for listening to the concerns of their constituents, debating policies, and voting on laws. Representatives must balance competing interests, consider expert opinions, and make informed decisions that benefit the greater good. This requires a high level of accountability, transparency, and responsiveness to the needs of the people.
Protection of Individual Rights

Another key feature of a republic is the protection of individual rights. A republic is founded on the principle that certain rights are inherent and inalienable, and that the government must protect and respect these rights. This includes the right to free speech, freedom of assembly, and the right to a fair trial. The protection of individual rights ensures that citizens are treated fairly and justly, and that the government does not abuse its power.
The Importance of Constitutional Safeguards
In a republic, constitutional safeguards play a crucial role in protecting individual rights. A constitution sets out the fundamental principles and limits of government power, ensuring that the government does not overstep its authority. Constitutional safeguards, such as the separation of powers, checks and balances, and the rule of law, provide a framework for governance that protects individual rights and promotes accountability.
Rule of Law

The rule of law is a fundamental feature of a republic, ensuring that the government and citizens are subject to the same laws and regulations. In a republic, laws are created through a transparent and accountable process, and are applied equally to all citizens. The rule of law promotes fairness, justice, and stability, and helps to prevent arbitrary and oppressive actions by the government.
The Significance of an Independent Judiciary
In a republic, an independent judiciary plays a critical role in upholding the rule of law. An independent judiciary ensures that the government does not abuse its power, and that citizens have access to fair and impartial justice. The judiciary acts as a check on the executive and legislative branches of government, ensuring that laws are constitutional and that individual rights are protected.
Checks and Balances

Checks and balances are a key feature of a republic, ensuring that power is distributed evenly among the different branches of government. In a republic, the executive, legislative, and judicial branches have distinct roles and responsibilities, and each branch has the power to check and balance the actions of the others. This helps to prevent any one branch of government from abusing its power, and promotes accountability and transparency.
The Importance of Separation of Powers
The separation of powers is a fundamental principle of a republic, ensuring that power is distributed evenly among the different branches of government. The separation of powers prevents any one branch of government from becoming too powerful, and promotes accountability and transparency. This helps to prevent corruption, abuse of power, and the erosion of individual rights.
Federalism

Federalism is a key feature of a republic, ensuring that power is distributed between the national government and smaller regional governments. In a republic, federalism allows for greater autonomy and self-governance at the regional level, while still maintaining a strong national government. Federalism promotes diversity, innovation, and accountability, and helps to prevent the concentration of power.
The Benefits of Decentralization
Decentralization is a fundamental principle of federalism, ensuring that power is distributed evenly between the national government and regional governments. Decentralization promotes greater autonomy and self-governance at the regional level, allowing for more responsive and accountable government. This helps to promote diversity, innovation, and economic growth, and reduces the risk of corruption and abuse of power.
As we conclude our exploration of the five key features of a republic form of government, it is clear that this system of governance offers numerous benefits and advantages. From the protection of individual rights to the promotion of accountability and transparency, a republic provides a framework for governance that is fair, just, and responsive to the needs of citizens. As citizens, it is essential that we understand and appreciate the principles of a republic, and work to promote and protect these principles in our own governance systems.
What is the primary difference between a republic and a democracy?
+A republic is a system of government where citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf, whereas a democracy is a system of government where citizens vote directly on laws and policies.
What is the role of the judiciary in a republic?
+The judiciary plays a critical role in upholding the rule of law and ensuring that the government does not abuse its power. An independent judiciary acts as a check on the executive and legislative branches of government, ensuring that laws are constitutional and that individual rights are protected.
What is the significance of federalism in a republic?
+Federalism ensures that power is distributed between the national government and smaller regional governments, promoting greater autonomy and self-governance at the regional level. This helps to promote diversity, innovation, and accountability, and reduces the risk of corruption and abuse of power.