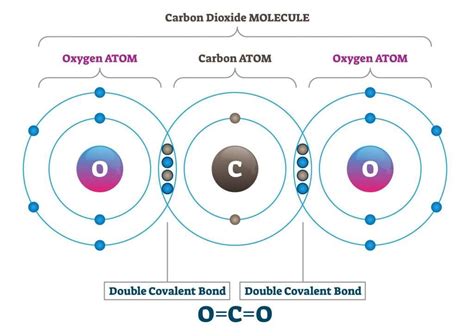
Carbon is the backbone of life on Earth, and its unique ability to form covalent bonds with other elements is the key to its versatility. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond where two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a stable molecule. Carbon's ability to form covalent bonds with a wide range of elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and more, makes it an ideal element for creating complex molecules.

Carbon's unique properties, such as its small size and moderate electronegativity, allow it to form covalent bonds with ease. This is evident in the many different types of carbon-based molecules that exist in nature, including biomolecules like DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates. In fact, it's estimated that there are over 10 million known carbon-based compounds, and this number is constantly growing as new compounds are discovered and synthesized.
Why Carbon Forms Covalent Bonds So Easily
So, why is carbon so good at forming covalent bonds? There are several reasons for this:
- Atomic size: Carbon has a relatively small atomic size, which allows it to form bonds with a wide range of elements. This is because smaller atoms have a higher electron density, making it easier for them to share electrons with other atoms.
- Electronegativity: Carbon has a moderate electronegativity value, which means it's not too eager to gain or lose electrons. This allows it to form stable bonds with other elements that have different electronegativity values.
- Valence electrons: Carbon has four valence electrons, which are the electrons in its outermost energy level. This allows it to form four covalent bonds with other atoms, making it an ideal element for creating complex molecules.
Examples of Carbon-Based Molecules
Carbon-based molecules are all around us, and they play a vital role in many different aspects of life. Here are a few examples:
- DNA: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a long, complex molecule that contains the genetic instructions for all living organisms. It's composed of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus atoms, and its structure is based on a repeating pattern of sugar and phosphate molecules.
- Proteins: Proteins are complex molecules that are composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of life. They're found in all living organisms and play a vital role in many different biological processes, including enzyme activity, structural support, and transport of molecules.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are a type of biomolecule that's composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They're an important source of energy for many living organisms and are found in a wide range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, and grains.

Carbon's Role in the Environment
Carbon plays a vital role in the environment, and its ability to form covalent bonds with other elements is essential for many different ecosystem processes. Here are a few examples:
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. It involves the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, and it's essential for life on Earth.
- Carbon cycle: The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. It's an essential process that helps regulate the Earth's climate and weather patterns.
- Soil formation: Soil is a complex ecosystem that's composed of carbon-based molecules, including humus, which is a type of organic matter that's formed from decomposed plant and animal material.

Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have a significant impact on the carbon cycle. Here are a few examples:
- Greenhouse gases: The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and contribute to climate change.
- Deforestation: Deforestation is the clearance of forests, usually for agricultural purposes. It releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and reduces the ability of forests to act as carbon sinks.
Conclusion: The Importance of Carbon in Covalent Bonds
In conclusion, carbon's ability to form covalent bonds with other elements is essential for life on Earth. Its unique properties, such as its small size and moderate electronegativity, make it an ideal element for creating complex molecules. Carbon-based molecules play a vital role in many different aspects of life, including biology, ecology, and the environment.

We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of carbon's role in covalent bonds. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out.
What is the main reason why carbon forms covalent bonds so easily?
+The main reason why carbon forms covalent bonds so easily is due to its small atomic size and moderate electronegativity value.
What are some examples of carbon-based molecules?
+Some examples of carbon-based molecules include DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates.
How does human activity impact the carbon cycle?
+Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and reduce the ability of forests to act as carbon sinks.