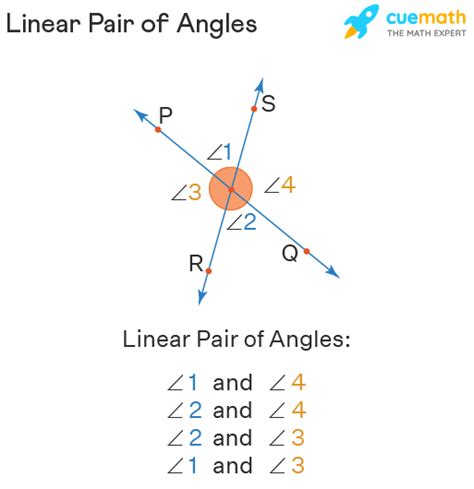
Linear pairs are a fundamental concept in geometry, and understanding their properties can help you solve various math problems. In this article, we'll delve into the world of linear pairs, exploring what they are, how they're formed, and their key characteristics.
When two angles form a linear pair, they share a common vertex and are adjacent to each other. This means that the angles are side by side, with one angle's vertex being the endpoint of the other angle's side. Linear pairs are also known as supplementary angles, as their measures add up to 180 degrees.

What is a Linear Pair?
A linear pair is formed when two angles share a common vertex and are adjacent to each other. The angles can be acute, right, or obtuse, but they must be supplementary, meaning their measures add up to 180 degrees. This is the key characteristic of linear pairs, and it's essential to remember this when solving math problems.

Types of Linear Pairs
There are several types of linear pairs, including:
- Complementary Linear Pairs: These are linear pairs where the two angles are complementary, meaning their measures add up to 90 degrees.
- Supplementary Linear Pairs: These are linear pairs where the two angles are supplementary, meaning their measures add up to 180 degrees.
- Right Linear Pairs: These are linear pairs where one angle is a right angle (90 degrees), and the other angle is also a right angle.

Properties of Linear Pairs
Linear pairs have several key properties that are essential to understand:
- Supplementary Angles: Linear pairs are supplementary, meaning their measures add up to 180 degrees.
- Common Vertex: Linear pairs share a common vertex.
- Adjacent Angles: Linear pairs are adjacent to each other.

Real-World Applications of Linear Pairs
Linear pairs have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: Linear pairs are used in building design to create symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing structures.
- Engineering: Linear pairs are used in engineering to design and build bridges, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Art: Linear pairs are used in art to create balanced and harmonious compositions.

Solving Math Problems Involving Linear Pairs
Solving math problems involving linear pairs requires a deep understanding of their properties and characteristics. Here are some tips to help you solve these problems:
- Identify the Linear Pair: Identify the two angles that form the linear pair and determine their relationship.
- Use the Properties of Linear Pairs: Use the properties of linear pairs, such as supplementary angles and common vertex, to solve the problem.
- Apply Mathematical Operations: Apply mathematical operations, such as addition and subtraction, to solve the problem.

Example Problems
Here are some example problems to help you understand how to solve math problems involving linear pairs:
- Problem 1: If two angles form a linear pair and one angle measures 60 degrees, what is the measure of the other angle?
- Problem 2: If two angles form a linear pair and one angle measures 120 degrees, what is the measure of the other angle?

Conclusion
In conclusion, linear pairs are a fundamental concept in geometry, and understanding their properties and characteristics is essential to solving math problems. By identifying the linear pair, using the properties of linear pairs, and applying mathematical operations, you can solve a wide range of math problems involving linear pairs.
If you have any questions or need further clarification on linear pairs, please don't hesitate to ask. Share your thoughts and experiences with linear pairs in the comments section below.
What is a linear pair in geometry?
+A linear pair is formed when two angles share a common vertex and are adjacent to each other. The angles can be acute, right, or obtuse, but they must be supplementary, meaning their measures add up to 180 degrees.
What are the properties of linear pairs?
+Linear pairs have several key properties, including supplementary angles, common vertex, and adjacent angles.
How do I solve math problems involving linear pairs?
+To solve math problems involving linear pairs, identify the linear pair, use the properties of linear pairs, and apply mathematical operations.