The human body is a complex and fascinating machine, made up of intricate systems and structures that work together to maintain overall health and function. At the most basic level, the body is composed of tiny building blocks called cells, which come together to form tissues. In turn, these tissues unite to form organs, and organs work together to create organ systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of tissue formation, exploring how these tiny units come together to form the complex structures that make up the human body.
From Cells to Tissues
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and they are the building blocks of all living organisms. In the human body, there are over 200 different types of cells, each with unique functions and characteristics. When cells with similar functions and characteristics come together, they form a tissue. There are four main types of tissue in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
Tissues are formed through a process called histogenesis, which involves the differentiation and organization of cells into specific patterns and structures. During histogenesis, cells undergo a series of changes, including proliferation, differentiation, and migration, which ultimately lead to the formation of a tissue. The type of tissue that forms depends on the specific functions and characteristics of the cells involved.
Forming Organs
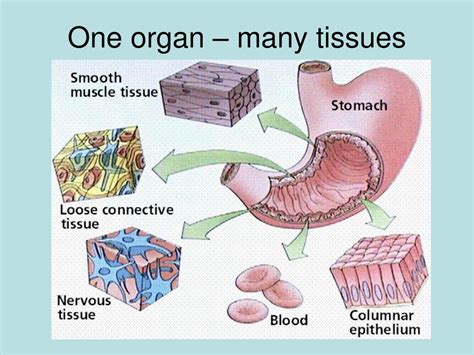
When two or more types of tissue come together, they form an organ. Organs are self-contained structures that perform specific functions necessary for the maintenance of life. Examples of organs include the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys. Each organ is made up of multiple types of tissue, which work together to perform the organ's specific functions.
The process of organ formation, also known as organogenesis, involves the coordinated development and organization of multiple types of tissue. During organogenesis, tissues undergo a series of complex interactions, including cell signaling, differentiation, and migration, which ultimately lead to the formation of a functional organ.
Organ Systems
When multiple organs work together to perform a specific function or set of functions, they form an organ system. Organ systems are groups of organs that work together to maintain homeostasis, or a stable internal environment, within the body. Examples of organ systems include the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems.
Organ systems are formed through a process called systemogenesis, which involves the coordinated development and organization of multiple organs. During systemogenesis, organs undergo a series of complex interactions, including cell signaling, differentiation, and migration, which ultimately lead to the formation of a functional organ system.
The Importance of Tissue Formation
Tissue formation is a critical process that occurs throughout the human lifespan, from embryonic development to adulthood. Without tissue formation, the body would not be able to repair damaged tissues, replace old or dying cells, or maintain overall health and function.
In addition to its role in development and maintenance, tissue formation also plays a critical role in disease and injury. When tissues are damaged or diseased, the body's ability to form new tissue is essential for recovery and healing. Understanding tissue formation and the processes involved is crucial for the development of new treatments and therapies for a wide range of diseases and injuries.

Types of Tissue Formation
There are several types of tissue formation, including:
- Epithelial tissue formation: Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that forms the lining of organs and glands. It is also found in the skin, where it forms the outer layer of the epidermis.
- Connective tissue formation: Connective tissue is a type of tissue that provides support and structure to the body. It is found in bone, cartilage, and fat tissue.
- Muscle tissue formation: Muscle tissue is a type of tissue that is responsible for movement and contraction. It is found in skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle.
- Nervous tissue formation: Nervous tissue is a type of tissue that is responsible for transmitting and processing information. It is found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
Stages of Tissue Formation
Tissue formation occurs in several stages, including:
- Proliferation: During this stage, cells divide and multiply, leading to an increase in cell number.
- Differentiation: During this stage, cells become specialized and acquire specific functions and characteristics.
- Migration: During this stage, cells move from one location to another, leading to the formation of a tissue.
- Organization: During this stage, cells come together to form a tissue, and the tissue acquires its specific structure and function.

Factors That Influence Tissue Formation
Several factors can influence tissue formation, including:
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence tissue formation by controlling the expression of specific genes involved in the process.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as temperature and pH, can influence tissue formation by affecting cell behavior and function.
- Hormones: Hormones can influence tissue formation by regulating cell growth and differentiation.

Conclusion
In conclusion, tissue formation is a critical process that occurs throughout the human lifespan. It is essential for the development and maintenance of the body, and plays a critical role in disease and injury. Understanding tissue formation and the processes involved is crucial for the development of new treatments and therapies for a wide range of diseases and injuries.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of tissue formation and its importance in the human body. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is tissue formation?
+Tissue formation is the process by which cells come together to form a tissue, which is a group of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
What are the different types of tissue formation?
+There are four main types of tissue formation: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue formation.
What are the stages of tissue formation?
+The stages of tissue formation include proliferation, differentiation, migration, and organization.