The human body is equipped with a remarkable digestive system that enables us to break down complex foods into simple nutrients. One of the key players in this process is pepsin, a digestive enzyme that plays a crucial role in protein digestion. But have you ever wondered how pepsin is formed in the first place? The answer lies in the conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin, a fascinating process that occurs in the stomach. In this article, we will delve into the world of pepsinogen conversion to pepsin, exploring the activation process, its significance, and the role it plays in our digestive health.

The Pepsinogen-Pepsin Cascade
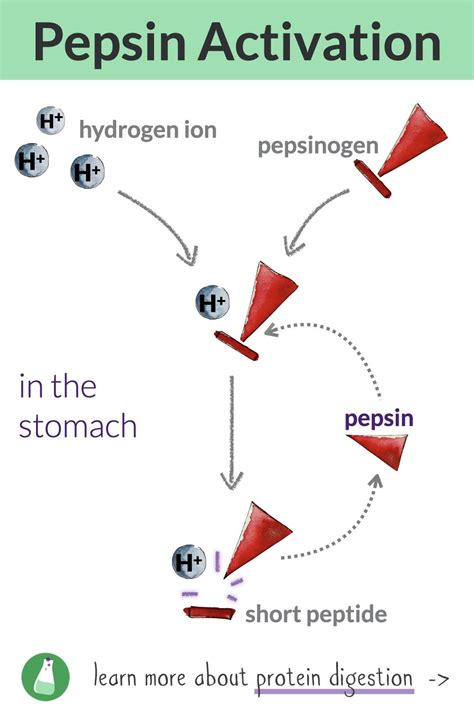
Pepsinogen is an inactive precursor to pepsin, produced by the chief cells in the stomach lining. It is a zymogen, a type of enzyme that requires activation to become functional. The conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin is a complex process that involves a series of molecular interactions. When pepsinogen is released into the stomach lumen, it comes into contact with hydrochloric acid (HCl) and existing pepsin molecules. The acidic environment triggers a conformational change in pepsinogen, allowing it to bind to HCl and existing pepsin molecules.
The Activation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The activation process of pepsinogen to pepsin involves several key steps:
Step 1: Release of Pepsinogen
Pepsinogen is released from the chief cells in the stomach lining in response to food intake. This is triggered by the release of gastrin, a hormone that stimulates the chief cells to produce pepsinogen.
Step 2: Binding to Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Pepsinogen binds to HCl in the stomach lumen, which triggers a conformational change in the molecule. This allows pepsinogen to bind to existing pepsin molecules.
Step 3: Binding to Existing Pepsin Molecules
Pepsinogen binds to existing pepsin molecules, which facilitates the activation process. This binding causes a conformational change in pepsinogen, allowing it to become active.
Step 4: Autocatalytic Activation
The bound pepsinogen molecule undergoes autocatalytic activation, where it cleaves itself to form active pepsin. This process is facilitated by the existing pepsin molecules, which act as catalysts.

Significance of Pepsinogen Conversion to Pepsin
The conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin is a crucial step in protein digestion. Pepsin plays a key role in breaking down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids, which can then be absorbed by the body. Without this process, protein digestion would be severely impaired, leading to malabsorption and other digestive disorders.
Role of Pepsinogen Conversion to Pepsin in Digestive Health
The pepsinogen-pepsin cascade plays a critical role in maintaining digestive health. It allows the body to break down proteins efficiently, which is essential for the absorption of essential amino acids. Any disruption to this process can lead to digestive disorders, such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and malabsorption.
Factors Affecting Pepsinogen Conversion to Pepsin
Several factors can affect the conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin, including:
pH Levels
The pH levels in the stomach lumen play a critical role in the activation of pepsinogen. The optimal pH for pepsinogen activation is between 2 and 3, which is maintained by the secretion of HCl.
Existing Pepsin Molecules
The presence of existing pepsin molecules is essential for the activation of pepsinogen. Without these molecules, the activation process would be severely impaired.
Gastrin Levels
Gastrin levels play a critical role in regulating pepsinogen production. Low gastrin levels can lead to impaired pepsinogen production, while high levels can stimulate excessive production.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin is a complex process that plays a critical role in protein digestion. Understanding this process is essential for appreciating the importance of digestive health and the role that pepsin plays in maintaining it. By recognizing the factors that affect pepsinogen conversion to pepsin, we can take steps to promote digestive health and prevent disorders.
FAQs
What is pepsinogen?
+Pepsinogen is an inactive precursor to pepsin, a digestive enzyme that plays a crucial role in protein digestion.
How is pepsinogen converted to pepsin?
+Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin through a complex process involving the binding of HCl and existing pepsin molecules, followed by autocatalytic activation.
What is the significance of pepsinogen conversion to pepsin?
+The conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin is crucial for protein digestion, allowing the body to break down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the pepsinogen-pepsin cascade and its significance in digestive health. If you have any further questions or would like to share your thoughts, please leave a comment below.