Unlocking Silicon's Electron Configuration in 4 Easy Steps
Silicon, a metalloid element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14, is one of the most abundant elements in the Earth's crust. Its unique electron configuration plays a crucial role in its chemical properties and reactivity. In this article, we will delve into the world of electron configuration and explore the steps to unlock silicon's electron configuration.
Silicon's electron configuration is a vital concept in chemistry and physics, as it helps us understand the element's behavior and interactions with other elements. By grasping the electron configuration of silicon, we can better comprehend its role in various applications, including electronics, solar cells, and computer chips. In this article, we will break down the process of unlocking silicon's electron configuration into four easy-to-follow steps.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics of Electron Configuration

Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. The electrons occupy specific energy levels or orbitals, which are described by their principal quantum number (n), azimuthal quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (m). The electron configuration of an atom is a vital concept in understanding its chemical properties and reactivity.
To unlock silicon's electron configuration, we need to understand the basic principles of electron configuration. The electrons in an atom occupy specific energy levels, which are filled in a specific order. The order of filling is determined by the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels. The electrons also follow the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
Key Takeaways:
- Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom.
- Electrons occupy specific energy levels or orbitals.
- The electron configuration of an atom determines its chemical properties and reactivity.
Step 2: Identifying Silicon's Atomic Number and Electron Count
To unlock silicon's electron configuration, we need to identify its atomic number and electron count. Silicon's atomic number is 14, which means it has 14 protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons, so silicon has 14 electrons.
The electron count is a critical piece of information in determining the electron configuration of an atom. With 14 electrons, silicon's electron configuration will involve the filling of energy levels up to the third energy level.
Key Takeaways:
- Silicon's atomic number is 14.
- Silicon has 14 electrons in a neutral atom.
- The electron count is critical in determining the electron configuration.
Step 3: Applying the Aufbau Principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle

To unlock silicon's electron configuration, we need to apply the Aufbau principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle. The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels, while the Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
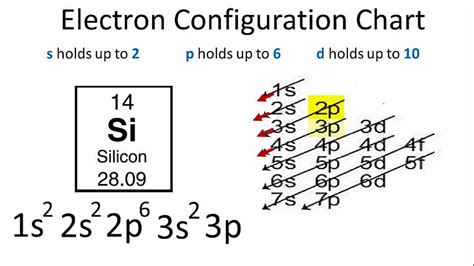
By applying these principles, we can fill the energy levels of silicon with its 14 electrons. The energy levels are filled in the following order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p. The 1s energy level is filled with two electrons, the 2s energy level is filled with two electrons, the 2p energy level is filled with six electrons, the 3s energy level is filled with two electrons, and the 3p energy level is filled with two electrons.
Key Takeaways:
- The Aufbau principle determines the order of filling energy levels.
- The Pauli Exclusion Principle determines the arrangement of electrons in energy levels.
- The energy levels are filled in a specific order.
Step 4: Writing Silicon's Electron Configuration
Finally, we can write silicon's electron configuration by listing the energy levels and the number of electrons in each level. Silicon's electron configuration is:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p²
This electron configuration shows that silicon has a full outer energy level, which makes it relatively stable. The electron configuration also explains silicon's chemical properties and reactivity.
Key Takeaways:
- Silicon's electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p².
- The electron configuration determines silicon's chemical properties and reactivity.
By following these four easy steps, we have unlocked silicon's electron configuration. Understanding the electron configuration of silicon is crucial in understanding its role in various applications, including electronics, solar cells, and computer chips.
What is electron configuration?
+Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
+The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
We hope this article has helped you understand the electron configuration of silicon. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!