Understanding the Formation of Rocks

Rocks are the building blocks of our planet, and understanding how they form is essential to grasping the fundamental processes that shape our Earth. One of the primary ways rocks form is through the crystallization of magma, a process that involves the cooling and solidification of molten rock beneath the Earth's surface. In this article, we will delve into the details of magma crystallization and explore the different types of rocks that form through this process.
The Magma Crystallization Process
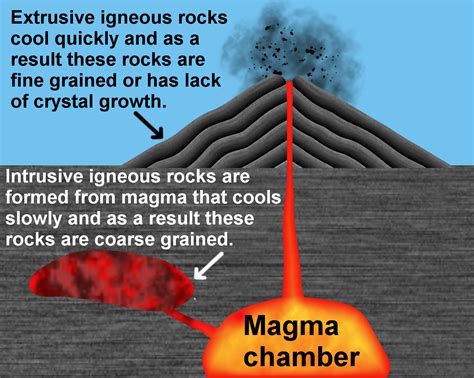
Magma crystallization occurs when molten rock cools and solidifies, either beneath the Earth's surface or as a result of volcanic activity. This process involves the slow cooling of magma, allowing minerals to crystallize and come together to form a solid rock. The rate at which the magma cools plays a significant role in determining the type of rock that forms. Rapid cooling results in the formation of fine-grained rocks, while slow cooling produces coarse-grained rocks.
The Role of Temperature and Pressure

Temperature and pressure are two critical factors that influence the magma crystallization process. As magma cools, the minerals within it begin to crystallize and settle out of the solution. The rate at which this occurs depends on the temperature and pressure conditions. Higher temperatures and pressures can slow down the crystallization process, resulting in the formation of larger crystals.
Types of Rocks Formed Through Magma Crystallization
Magma crystallization produces a wide range of rock types, including igneous rocks, which are further divided into intrusive and extrusive rocks.
- Intrusive Rocks: These rocks form when magma cools and solidifies beneath the Earth's surface. Examples of intrusive rocks include granite, diorite, and gabbro.
- Extrusive Rocks: These rocks form when magma cools and solidifies on the Earth's surface, often as a result of volcanic activity. Examples of extrusive rocks include basalt, andesite, and obsidian.
Factors Influencing Rock Formation

Several factors influence the formation of rocks through magma crystallization, including:
- Chemical Composition: The chemical makeup of the magma determines the type of minerals that will crystallize and the resulting rock type.
- Temperature: The temperature at which the magma cools affects the rate of crystallization and the resulting rock texture.
- Pressure: The pressure at which the magma cools influences the rate of crystallization and the resulting rock texture.
- Time: The amount of time available for crystallization affects the size and shape of the minerals that form.
Examples of Rocks Formed Through Magma Crystallization
- Granite: A coarse-grained, intrusive rock that forms when magma cools slowly beneath the Earth's surface.
- Basalt: A fine-grained, extrusive rock that forms when magma cools rapidly on the Earth's surface.
- Gabbro: A coarse-grained, intrusive rock that forms when magma cools slowly beneath the Earth's surface.
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the formation of rocks through magma crystallization is a complex process that involves the cooling and solidification of molten rock. Understanding this process is essential to grasping the fundamental processes that shape our planet. Future research directions may include the study of the chemical and physical processes that occur during magma crystallization, as well as the development of new techniques for analyzing and interpreting rock formations.
Getting Involved
We hope this article has sparked your interest in the fascinating world of rock formation. Whether you're a seasoned geologist or just starting to explore the Earth sciences, there are many ways to get involved and learn more. Here are a few suggestions:
- Join a geological society: Many countries have geological societies that offer membership, publications, and opportunities to participate in field trips and conferences.
- Participate in citizen science projects: There are many citizen science projects that allow individuals to contribute to geological research and exploration.
- Take a geology course: Consider taking a course in geology or Earth sciences to learn more about the fundamentals of rock formation and the processes that shape our planet.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about rock formation and magma crystallization in the comments below. What aspects of this topic would you like to learn more about? Do you have any personal experiences or observations related to rock formation? Let's start a conversation!
What is magma crystallization?
+Magma crystallization is the process by which molten rock cools and solidifies, resulting in the formation of rocks.
What factors influence rock formation through magma crystallization?
+The factors that influence rock formation through magma crystallization include chemical composition, temperature, pressure, and time.
What types of rocks are formed through magma crystallization?
+Rocks formed through magma crystallization include igneous rocks, such as granite, basalt, and gabbro.