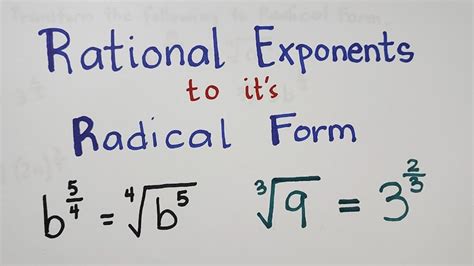Radicals, also known as roots, are a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and geometry. However, dealing with radicals can be intimidating, especially when it comes to simplifying and manipulating them. One way to make radicals more manageable is by expressing them in exponential form. In this article, we will explore the exponential form of radicals, its benefits, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to convert radicals to exponential form.
What are Radicals?

Radicals are mathematical expressions that represent the root of a number. The most common type of radical is the square root, denoted by the symbol √. For example, √16 represents the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. Other types of radicals include cube roots, fourth roots, and so on.
The Problem with Radicals
While radicals are essential in mathematics, they can be challenging to work with, especially when dealing with complex expressions. One of the main issues with radicals is that they can be difficult to simplify and manipulate. For instance, simplifying an expression like √(2 + √3) can be a daunting task.
Exponential Form of Radicals

One way to overcome the challenges of working with radicals is by expressing them in exponential form. The exponential form of a radical is a way of writing the radical using exponents instead of the radical symbol. For example, the square root of 16 can be expressed as 16^(1/2) or 2^2.
Benefits of Exponential Form
Expressing radicals in exponential form has several benefits, including:
- Simplifying complex expressions: Exponential form can help simplify complex expressions involving radicals, making them easier to work with.
- Easier manipulation: Exponential form allows for easier manipulation of radicals, making it simpler to perform operations like multiplication and division.
- Improved readability: Exponential form can make expressions more readable, reducing the visual clutter of radical symbols.
Converting Radicals to Exponential Form

Converting radicals to exponential form is a straightforward process. Here are the steps:
- Identify the type of radical: Determine the type of radical you are dealing with, such as a square root, cube root, or fourth root.
- Determine the index: The index of a radical is the number that indicates the type of root. For example, the index of a square root is 2, while the index of a cube root is 3.
- Rewrite the radical: Rewrite the radical using the exponential form. For example, √16 can be rewritten as 16^(1/2).
- Simplify the expression: Simplify the expression by evaluating the exponent.
Examples
Here are some examples of converting radicals to exponential form:
- √16 = 16^(1/2) = 2^2
- ∛27 = 27^(1/3) = 3^3
- ⁴√256 = 256^(1/4) = 4^4
Working with Exponential Form

Once you have expressed a radical in exponential form, you can work with it like any other exponential expression. Here are some examples:
- Multiplication: 2^2 × 3^3 = 2^2 × 3^3 = 12^5
- Division: 4^4 ÷ 2^2 = 4^4 ÷ 2^2 = 2^2
- Exponentiation: (2^2)^3 = 2^2 × 2^3 = 2^5
Common Mistakes
When working with exponential form, it's essential to avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Incorrectly converting radicals to exponential form
- Failing to simplify expressions
- Incorrectly applying exponent rules
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, expressing radicals in exponential form is a powerful way to simplify and manipulate complex expressions. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can convert radicals to exponential form and work with them like any other exponential expression. Remember to avoid common mistakes and practice working with exponential form to become more proficient.
Call to Action
Now that you have learned about the exponential form of radicals, we encourage you to practice working with it. Try converting different types of radicals to exponential form and simplifying complex expressions. Share your experiences and questions in the comments below.
FAQ Section:
What is the exponential form of a radical?
+The exponential form of a radical is a way of writing the radical using exponents instead of the radical symbol.
How do I convert a radical to exponential form?
+To convert a radical to exponential form, identify the type of radical, determine the index, rewrite the radical using the exponential form, and simplify the expression.
What are the benefits of expressing radicals in exponential form?
+Expressing radicals in exponential form simplifies complex expressions, makes manipulation easier, and improves readability.