The pest management industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing concerns about public health, environmental sustainability, and property preservation. As a result, pest management professionals are under growing pressure to demonstrate their commitment to effective and responsible pest control practices. One crucial aspect of this commitment is maintaining accurate and comprehensive pest management records, particularly the NPMA 33 Form.

What is the NPMA 33 Form?
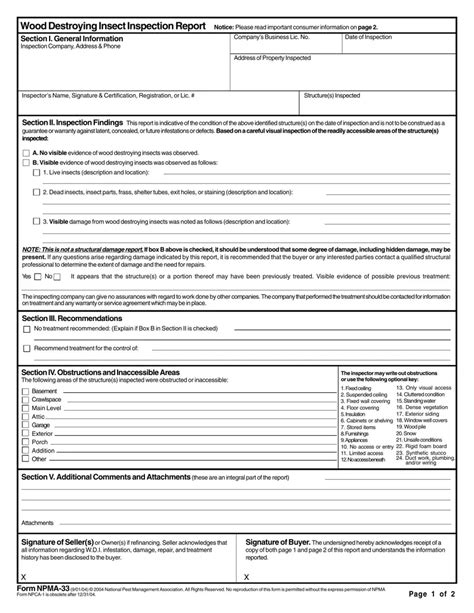
The NPMA 33 Form, also known as the "Wood-Destroying Insect (WDI) Inspection Report," is a standardized document used by pest management professionals to report on the presence or absence of wood-destroying insects, such as termites, in a given structure. Developed by the National Pest Management Association (NPMA), this form provides a framework for inspectors to gather and record essential information about the property, the inspection process, and any findings related to wood-destroying insects.
Importance of the NPMA 33 Form
The NPMA 33 Form plays a vital role in the pest management industry, serving several purposes:
- Risk assessment: The form helps inspectors identify potential risks associated with wood-destroying insects, enabling them to provide property owners with informed recommendations for mitigation and treatment.
- Regulatory compliance: Many states and local jurisdictions require pest management professionals to use the NPMA 33 Form or similar documents to report on WDI inspections. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure that inspections are conducted consistently and thoroughly.
- Insurance and financing: Lenders and insurers often require NPMA 33 Forms as part of the mortgage or insurance application process. This helps them assess the risk of termite damage and make informed decisions about coverage and lending.
Components of the NPMA 33 Form
The NPMA 33 Form is divided into several sections, each designed to capture specific information about the property and the inspection process.

- Section 1: Property Information: This section requires inspectors to provide details about the property, including the address, owner's name, and type of structure.
- Section 2: Inspection Information: Inspectors must record information about the inspection process, such as the date, time, and weather conditions.
- Section 3: Findings: This section is used to report on any signs of wood-destroying insects, including termite activity, damage, or evidence of previous treatments.
- Section 4: Recommendations: Based on their findings, inspectors provide recommendations for treatment, mitigation, or further inspection.
Benefits of Using the NPMA 33 Form
The NPMA 33 Form offers several benefits to pest management professionals, property owners, and regulatory agencies:
- Standardization: The form ensures that inspections are conducted consistently, reducing variability and increasing the accuracy of findings.
- Comprehensive reporting: The NPMA 33 Form captures essential information about the property and inspection process, providing a detailed record of the inspector's findings and recommendations.
- Risk management: By identifying potential risks associated with wood-destroying insects, the form helps property owners and insurers make informed decisions about mitigation and treatment.
Best Practices for Using the NPMA 33 Form
To ensure accurate and effective use of the NPMA 33 Form, pest management professionals should follow these best practices:

- Complete all sections thoroughly: Ensure that all sections of the form are fully completed, including the property information, inspection details, and findings.
- Use clear and concise language: Inspectors should use straightforward language when reporting their findings and recommendations.
- Include supporting documentation: Attach any supporting documentation, such as photographs or diagrams, to the form to provide additional context.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When using the NPMA 33 Form, pest management professionals should avoid the following common mistakes:
- Incomplete or inaccurate information: Failing to complete all sections of the form or providing inaccurate information can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretation of findings.
- Lack of supporting documentation: Failing to include supporting documentation can make it difficult for property owners and insurers to understand the inspector's findings and recommendations.
Conclusion
The NPMA 33 Form is a crucial tool for pest management professionals, providing a standardized framework for reporting on wood-destroying insect inspections. By understanding the components and benefits of the form, as well as best practices for its use, inspectors can ensure accurate and effective reporting, ultimately helping to protect property owners and the environment.
What is the purpose of the NPMA 33 Form?
+The NPMA 33 Form is used to report on the presence or absence of wood-destroying insects, such as termites, in a given structure.
Why is the NPMA 33 Form important?
+The NPMA 33 Form helps inspectors identify potential risks associated with wood-destroying insects, enabling them to provide property owners with informed recommendations for mitigation and treatment.
What are the benefits of using the NPMA 33 Form?
+The NPMA 33 Form offers several benefits, including standardization, comprehensive reporting, and risk management.