Carbon, one of the most versatile elements in the periodic table, is a fundamental building block of life on Earth. In its various forms, carbon plays a crucial role in shaping our planet's climate, ecosystems, and economies. In this article, we will delve into five distinct forms of carbon, focusing on CO2, and explore their characteristics, impacts, and relationships with our environment.
What is Carbon?

Carbon, denoted by the symbol C, is a nonmetallic element that exists in various forms, both naturally and synthetically. It is the sixth most abundant element in the universe, comprising approximately 0.02% of the Earth's crust. Carbon's unique chemical properties allow it to form a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex biomolecules.
The Role of Carbon in Climate Change
Carbon plays a pivotal role in regulating the Earth's climate. One of its most significant forms, carbon dioxide (CO2), is a potent greenhouse gas. As CO2 levels in the atmosphere increase, they trap more heat from the sun, leading to global warming and associated climate change impacts. Understanding the different forms of carbon is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change.
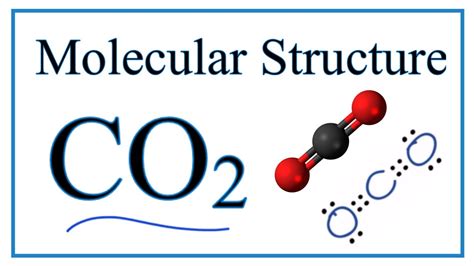
Forms of Carbon: CO2

Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the most abundant forms of carbon in the atmosphere. It is a colorless, odorless gas that occurs naturally in the Earth's atmosphere, primarily due to volcanic eruptions, respiration, and decomposition processes. Human activities, such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and land-use changes, have significantly increased CO2 emissions, leading to a sharp rise in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Impacts of CO2 on the Environment
Elevated CO2 levels in the atmosphere have far-reaching consequences for the environment:
- Global Warming: Excess CO2 traps heat, leading to rising global temperatures, more extreme weather events, and altered ecosystems.
- Ocean Acidification: CO2 absorption by oceans increases their acidity, harming marine life, especially coral reefs and shellfish.
- Water Cycle Disruptions: Changes in precipitation patterns and increased evaporation due to warmer temperatures impact water availability and quality.
Other Forms of Carbon: Diamonds, Graphite, and More

In addition to CO2, carbon exists in several other forms, each with unique properties and applications:
- Diamonds: Pure carbon crystals with exceptional hardness and thermal conductivity, used in jewelry, cutting tools, and electronic devices.
- Graphite: A soft, slippery form of carbon used in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes.
- Fullerenes: A family of carbon molecules with a hollow, spherical structure, discovered in 1985, with potential applications in nanotechnology and medicine.
- Carbon Nanotubes: Tiny, cylindrical structures composed of carbon atoms, exhibiting remarkable strength, conductivity, and thermal properties.
Carbon Cycle and its Importance
The carbon cycle refers to the continuous movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. Understanding the carbon cycle is crucial for managing carbon emissions, mitigating climate change, and maintaining ecosystem balance.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle

Human activities significantly influence the carbon cycle, primarily through:
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: Burning coal, oil, and gas releases massive amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Deforestation and Land-Use Changes: Clearance of forests and changes in land use reduce carbon sequestration and increase emissions.
- Agriculture and Soil Degradation: Intensive farming practices and soil erosion lead to soil carbon loss and increased emissions.
Mitigating Climate Change through Carbon Management
To address climate change, it is essential to manage carbon emissions and promote sustainable carbon cycle practices:
- Renewable Energy: Transitioning to solar, wind, and other low-carbon energy sources can significantly reduce CO2 emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Implementing technologies to capture and store CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial processes.
- Sustainable Land Use: Implementing practices like reforestation, agroforestry, and permaculture to enhance carbon sequestration and reduce emissions.
Conclusion: Embracing a Low-Carbon Future
In conclusion, understanding the different forms of carbon, particularly CO2, is crucial for addressing climate change and promoting a sustainable future. By acknowledging the importance of carbon management, we can work towards reducing emissions, conserving natural resources, and protecting the planet for future generations.
What is the most abundant form of carbon in the atmosphere?
+Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most abundant form of carbon in the atmosphere.
What are some natural sources of CO2 emissions?
+Natural sources of CO2 emissions include volcanic eruptions, respiration, and decomposition processes.
What is the role of carbon in the climate change process?
+Carbon, particularly CO2, plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and associated climate change impacts.