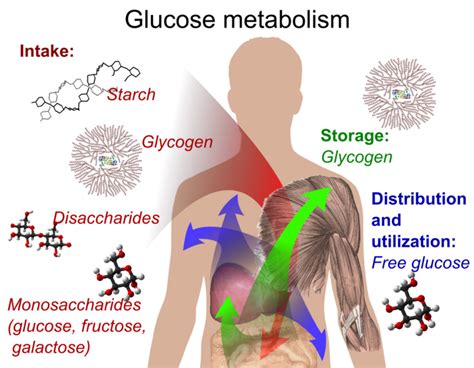
Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that serves as the primary storage form of glucose in the body. It is a vital component of energy metabolism, and its importance cannot be overstated. In this article, we will delve into the world of glycogen, exploring its structure, functions, benefits, and the process of glycogen synthesis and breakdown.

What is Glycogen?
Glycogen is a polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules bonded together through glycosidic linkages. It is synthesized in the liver and muscles from glucose molecules, using energy derived from ATP. Glycogen is often referred to as "animal starch" due to its structural similarity to plant starch.
Structure of Glycogen
Glycogen is a branched molecule, consisting of a core protein called glycogenin, surrounded by chains of glucose molecules. The glucose molecules are linked together through α-1,4-glycosidic bonds, forming a long chain. The chain is then branched at specific points, creating a tree-like structure. This branching allows for rapid synthesis and breakdown of glycogen.

Functions of Glycogen
Glycogen plays a crucial role in maintaining energy homeostasis in the body. Its primary functions include:
- Energy Storage: Glycogen serves as a readily mobilizable energy reserve, allowing for rapid release of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Regulation of Blood Sugar: Glycogen helps regulate blood sugar levels by storing excess glucose and releasing it when needed.
- Muscle Function: Glycogen is an essential energy source for muscle contraction and relaxation.
Benefits of Glycogen
Adequate glycogen storage has numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Endurance: Increased glycogen storage in muscles enhances endurance during prolonged exercise.
- Reduced Fatigue: Adequate glycogen levels help reduce fatigue and improve overall physical performance.
- Supports Weight Loss: Glycogen storage helps regulate appetite and supports weight loss efforts.

Glycogen Synthesis and Breakdown
Glycogen synthesis and breakdown are complex processes involving multiple enzymes and regulatory mechanisms.
- Glycogen Synthesis: Glycogen is synthesized from glucose molecules using energy derived from ATP. The process involves the enzyme glycogen synthase.
- Glycogen Breakdown: Glycogen is broken down into glucose molecules through the action of the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism
Glycogen metabolism is regulated by various hormones and signaling pathways, including:
- Insulin: Insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis and inhibits glycogen breakdown.
- Glucagon: Glucagon stimulates glycogen breakdown and inhibits glycogen synthesis.
- Adrenaline: Adrenaline stimulates glycogen breakdown and mobilization.

Practical Applications of Glycogen
Understanding glycogen metabolism has numerous practical applications, including:
- Sports Nutrition: Adequate glycogen storage is essential for optimal athletic performance.
- Weight Management: Glycogen storage plays a role in weight regulation and appetite control.
- Blood Sugar Management: Glycogen metabolism is critical for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.

Conclusion
In conclusion, glycogen is a vital component of energy metabolism, serving as the primary storage form of glucose in the body. Understanding glycogen structure, functions, benefits, and metabolism can provide valuable insights into maintaining optimal energy homeostasis, improving athletic performance, and regulating blood sugar levels.
If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What is the primary function of glycogen?
+The primary function of glycogen is to serve as a readily mobilizable energy reserve, allowing for rapid release of glucose into the bloodstream.
How is glycogen synthesized?
+Glycogen is synthesized from glucose molecules using energy derived from ATP. The process involves the enzyme glycogen synthase.
What are the benefits of adequate glycogen storage?
+Adequate glycogen storage has numerous benefits, including improved endurance, reduced fatigue, and support for weight loss efforts.