Water is essential for human life, and its unique properties make it a vital component of our planet's ecosystem. At its core, water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, which come together through various processes to form this life-giving substance. In this article, we will explore the five ways hydrogen and oxygen form water, shedding light on the fascinating chemistry behind this process.
Chemical Bonding: The Foundation of Water Formation

Water formation begins with the chemical bonding of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. This process involves the sharing of electrons between the atoms, resulting in a covalent bond. The oxygen atom, with its six valence electrons, seeks to complete its outer shell by sharing electrons with the hydrogen atoms, each of which has one valence electron. As the atoms bond, they form a stable molecule with a bent or V-shape structure, which is characteristic of water.
The Role of Electronegativity
The electronegativity of oxygen plays a crucial role in the formation of the water molecule. Oxygen's high electronegativity value (3.44) allows it to pull the shared electrons closer to itself, resulting in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom. This unequal sharing of electrons creates a polar molecule, which is essential for many of water's unique properties, such as its high surface tension and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
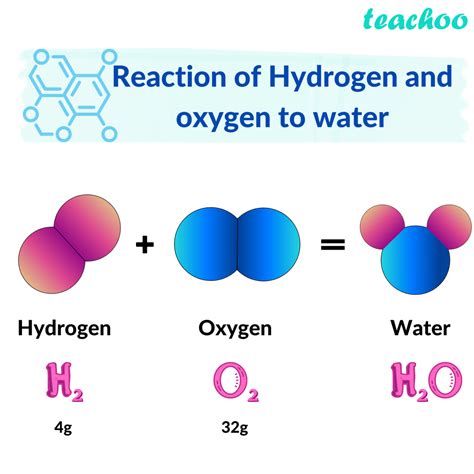
Method 1: Direct Combination of Hydrogen and Oxygen

One way hydrogen and oxygen form water is through their direct combination. This process occurs when hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with oxygen gas (O2) in the presence of a spark or flame. The reaction is highly exothermic, releasing a significant amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
This reaction is often used in industrial processes, such as the production of hydrogen peroxide, and in the laboratory to generate water for various experiments.
Method 2: Hydrolysis of Salts

Hydrolysis is another way hydrogen and oxygen form water. This process involves the reaction of a salt with water to produce an acid and a base. For example, the hydrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) produces hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
NaCl (s) + H2O (l) → HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq)
This reaction is essential in many biological processes, such as the digestion of food in the stomach, where hydrochloric acid helps break down proteins and other nutrients.
Method 3: Oxidation of Hydrogen-Containing Compounds

The oxidation of hydrogen-containing compounds is another method by which hydrogen and oxygen form water. This process involves the reaction of a compound containing hydrogen with oxygen to produce water and a new compound. For example, the oxidation of methane (CH4) produces carbon dioxide (CO2) and water.
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
This reaction is essential in many industrial processes, such as the production of energy through the combustion of fossil fuels.
Method 4: Electrolysis of Water

Electrolysis is the process by which an electric current is used to drive a chemical reaction. In the case of water, electrolysis involves the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. This process is often used in industrial applications, such as the production of hydrogen fuel cells.
2H2O (l) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
This reaction is also used in the laboratory to generate hydrogen and oxygen gases for various experiments.
Method 5: Biological Processes

Finally, hydrogen and oxygen form water through various biological processes. For example, during photosynthesis, plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, releasing water as a byproduct.
6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) → C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g)
This process is essential for life on Earth, as it provides energy and organic compounds for growth and development.
In conclusion, the formation of water through the combination of hydrogen and oxygen is a complex process that occurs through various methods, including direct combination, hydrolysis of salts, oxidation of hydrogen-containing compounds, electrolysis of water, and biological processes. Understanding these processes is essential for appreciating the importance of water in our daily lives and the natural world.
What is the chemical composition of water?
+Water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, with the chemical formula H2O.
What is the role of electronegativity in the formation of the water molecule?
+The electronegativity of oxygen allows it to pull the shared electrons closer to itself, resulting in a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom, creating a polar molecule.
What are some industrial applications of the direct combination of hydrogen and oxygen?
+The direct combination of hydrogen and oxygen is used in the production of hydrogen peroxide and in the laboratory to generate water for various experiments.