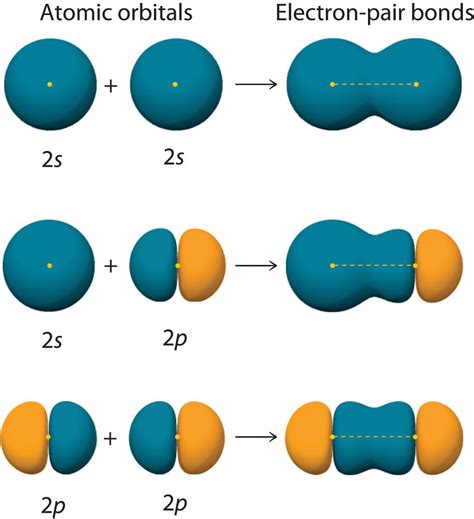
The world of chemistry is full of fascinating concepts that help us understand the behavior of atoms and molecules. One such concept is the formation of molecular orbitals through the overlap of hybrid orbitals. In this article, we will delve into the world of molecular orbital theory and explore how hybrid orbitals overlap to form molecular orbitals.
Understanding molecular orbitals is crucial in chemistry as it helps us predict the shape, polarity, and reactivity of molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed when atomic orbitals combine to form a new set of orbitals that describe the distribution of electrons in a molecule. Hybrid orbitals, on the other hand, are a set of orbitals that are formed by combining atomic orbitals of different types, such as s, p, and d orbitals.

What are Hybrid Orbitals?
Hybrid orbitals are a set of orbitals that are formed by combining atomic orbitals of different types. The most common types of hybrid orbitals are sp3, sp2, and sp. These hybrid orbitals are formed by combining one s orbital with one, two, or three p orbitals, respectively. The resulting hybrid orbitals have different shapes and energies than the original atomic orbitals.
For example, when one s orbital and one p orbital combine, they form two sp hybrid orbitals. These sp hybrid orbitals have a linear shape and are oriented at an angle of 180 degrees to each other. Similarly, when one s orbital and two p orbitals combine, they form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. These sp2 hybrid orbitals have a trigonal planar shape and are oriented at an angle of 120 degrees to each other.
Types of Hybrid Orbitals
There are several types of hybrid orbitals, including:
- sp3 hybrid orbitals: These hybrid orbitals are formed by combining one s orbital with three p orbitals. They have a tetrahedral shape and are oriented at an angle of 109.5 degrees to each other.
- sp2 hybrid orbitals: These hybrid orbitals are formed by combining one s orbital with two p orbitals. They have a trigonal planar shape and are oriented at an angle of 120 degrees to each other.
- sp hybrid orbitals: These hybrid orbitals are formed by combining one s orbital with one p orbital. They have a linear shape and are oriented at an angle of 180 degrees to each other.

How do Hybrid Orbitals Overlap to Form Molecular Orbitals?
When two atoms bond together, their hybrid orbitals overlap to form molecular orbitals. The overlap of hybrid orbitals results in the formation of a new set of orbitals that describe the distribution of electrons in the molecule. The molecular orbitals are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the individual atoms.
For example, when two sp3 hybrid orbitals overlap, they form a sigma (σ) molecular orbital. The sigma molecular orbital has a symmetrical shape and is oriented along the bond axis. Similarly, when two sp2 hybrid orbitals overlap, they form a sigma (σ) molecular orbital and a pi (π) molecular orbital. The pi molecular orbital has a nodal plane perpendicular to the bond axis.
Types of Molecular Orbitals
There are several types of molecular orbitals, including:
- Sigma (σ) molecular orbitals: These molecular orbitals are symmetrical and are oriented along the bond axis.
- Pi (π) molecular orbitals: These molecular orbitals have a nodal plane perpendicular to the bond axis.
- Delta (δ) molecular orbitals: These molecular orbitals have a nodal plane perpendicular to the bond axis and a nodal cone along the bond axis.

Benefits of Understanding Molecular Orbitals
Understanding molecular orbitals has several benefits, including:
- Predicting molecular shape: Molecular orbitals help us predict the shape of a molecule, which is crucial in understanding its reactivity and properties.
- Predicting molecular polarity: Molecular orbitals help us predict the polarity of a molecule, which is crucial in understanding its reactivity and properties.
- Understanding chemical reactivity: Molecular orbitals help us understand the chemical reactivity of a molecule, which is crucial in understanding its properties and behavior.
Applications of Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular orbital theory has several applications, including:
- Understanding the behavior of molecules in different environments
- Predicting the properties of molecules
- Designing new molecules with specific properties
- Understanding the reactivity of molecules

Conclusion
In conclusion, the overlap of hybrid orbitals to form molecular orbitals is a crucial concept in chemistry. Understanding molecular orbitals helps us predict the shape, polarity, and reactivity of molecules, which is essential in understanding their properties and behavior. The benefits of understanding molecular orbitals are numerous, and its applications are diverse.
We hope this article has helped you understand the concept of hybrid orbitals and molecular orbitals. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to ask.
What are hybrid orbitals?
+Hybrid orbitals are a set of orbitals that are formed by combining atomic orbitals of different types.
How do hybrid orbitals overlap to form molecular orbitals?
+When two atoms bond together, their hybrid orbitals overlap to form molecular orbitals.
What are the benefits of understanding molecular orbitals?
+Understanding molecular orbitals helps us predict the shape, polarity, and reactivity of molecules.