Converting standard form to slope-intercept form is a crucial skill in algebra, and it's used extensively in graphing lines, solving systems of equations, and modeling real-world problems. In this article, we'll delve into the world of linear equations, explore the differences between standard form and slope-intercept form, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to convert standard form to slope-intercept form easily.
What is Standard Form?

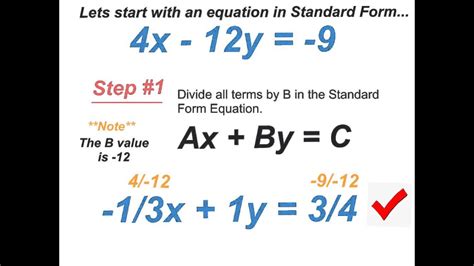
Standard form, also known as general form, is a way of writing linear equations in the form:
Ax + By = C
where A, B, and C are constants, and x and y are variables. This form is useful for solving systems of equations and finding the x- and y-intercepts of a line.
What is Slope-Intercept Form?

Slope-intercept form, on the other hand, is a way of writing linear equations in the form:
y = mx + b
where m is the slope of the line, and b is the y-intercept. This form is useful for graphing lines, finding the equation of a line given two points, and identifying the slope and y-intercept of a line.
Why Convert Standard Form to Slope-Intercept Form?

Converting standard form to slope-intercept form is essential because it allows us to:
- Graph lines more easily
- Find the slope and y-intercept of a line
- Identify the x- and y-intercepts of a line
- Solve systems of equations more efficiently
- Model real-world problems more accurately
How to Convert Standard Form to Slope-Intercept Form

Converting standard form to slope-intercept form involves a few simple steps:
- Rearrange the equation: Rearrange the standard form equation to isolate y on one side of the equation.
Example: 2x + 3y = 5 → 3y = -2x + 5
- Divide by the coefficient of y: Divide both sides of the equation by the coefficient of y to solve for y.
Example: 3y = -2x + 5 → y = (-2/3)x + 5/3
- Simplify the equation: Simplify the equation to its simplest form.
Example: y = (-2/3)x + 5/3 → y = (-2/3)x + 1.67
Example Problems
Let's practice converting standard form to slope-intercept form with a few example problems:
- Convert the equation 4x - 2y = 8 to slope-intercept form.
Solution: 2y = 4x - 8 → y = 2x - 4
- Convert the equation x + 5y = 3 to slope-intercept form.
Solution: 5y = -x + 3 → y = (-1/5)x + 3/5
- Convert the equation 2x - 3y = 9 to slope-intercept form.
Solution: 3y = 2x - 9 → y = (2/3)x - 3
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When converting standard form to slope-intercept form, it's easy to make mistakes. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Forgetting to divide by the coefficient of y
- Not simplifying the equation to its simplest form
- Not rearranging the equation to isolate y on one side
- Not checking for errors in the conversion process
Conclusion

Converting standard form to slope-intercept form is a crucial skill in algebra, and it's used extensively in graphing lines, solving systems of equations, and modeling real-world problems. By following the simple steps outlined in this article, you'll be able to convert standard form to slope-intercept form easily and accurately.
We hope this article has helped you understand the importance of converting standard form to slope-intercept form and has provided you with the skills and confidence to tackle this task with ease.
Do you have any questions or comments about converting standard form to slope-intercept form? Share them with us in the comments section below!
What is the main difference between standard form and slope-intercept form?
+The main difference between standard form and slope-intercept form is the way the equation is written. Standard form is written in the form Ax + By = C, while slope-intercept form is written in the form y = mx + b.
Why is it important to convert standard form to slope-intercept form?
+Converting standard form to slope-intercept form is important because it allows us to graph lines more easily, find the slope and y-intercept of a line, and solve systems of equations more efficiently.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when converting standard form to slope-intercept form?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when converting standard form to slope-intercept form include forgetting to divide by the coefficient of y, not simplifying the equation to its simplest form, and not rearranging the equation to isolate y on one side.