Understanding the properties and behavior of elements is crucial in the field of chemistry, and one of the key concepts in this realm is the formation of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are chemical bonds that involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. The number and type of covalent bonds that an element can form are determined by its electron configuration, particularly the number of valence electrons.
In this article, we will delve into the world of covalent bonds and explore the essential covalent bonds that each element generally forms. We will also examine the factors that influence the formation of these bonds and provide examples to illustrate the concepts.
What are Covalent Bonds?

Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. This sharing of electrons leads to the formation of a stable molecule, where the atoms are held together by the shared electrons. Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved.
Factors Influencing Covalent Bond Formation
Several factors influence the formation of covalent bonds, including:
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
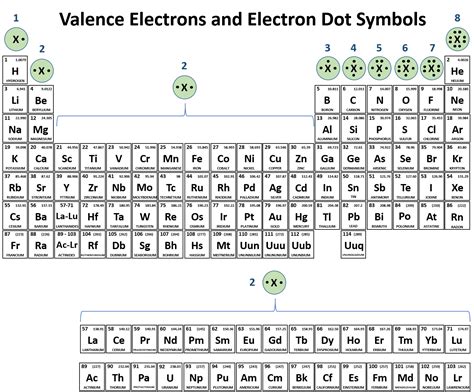
- Valence electrons: The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom.
- Atomic size: The size of the atom, which affects the distance between the nuclei and the electrons.
- Bond energy: The energy required to break a covalent bond.
Essential Covalent Bonds Formed by Each Element

Each element has a unique set of covalent bonds that it generally forms. Here are 8 essential covalent bonds formed by each element:
1. Hydrogen (H)
- Forms 1 covalent bond with other atoms, typically with oxygen, nitrogen, or carbon.
- Examples: H2O (water), NH3 (ammonia), CH4 (methane).
2. Carbon (C)
- Forms 4 covalent bonds with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, oxygen, or other carbon atoms.
- Examples: CH4 (methane), CO2 (carbon dioxide), C6H12O6 (glucose).
3. Nitrogen (N)
- Forms 3 covalent bonds with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, oxygen, or carbon.
- Examples: NH3 (ammonia), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), C6H12O6 (glucose).
4. Oxygen (O)
- Forms 2 covalent bonds with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, carbon, or other oxygen atoms.
- Examples: H2O (water), CO2 (carbon dioxide), O2 (oxygen gas).
5. Fluorine (F)
- Forms 1 covalent bond with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, carbon, or other fluorine atoms.
- Examples: HF (hydrogen fluoride), CF4 (carbon tetrafluoride), F2 (fluorine gas).
6. Chlorine (Cl)
- Forms 1 covalent bond with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, carbon, or other chlorine atoms.
- Examples: HCl (hydrogen chloride), CCl4 (carbon tetrachloride), Cl2 (chlorine gas).
7. Bromine (Br)
- Forms 1 covalent bond with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, carbon, or other bromine atoms.
- Examples: HBr (hydrogen bromide), CBr4 (carbon tetrabromide), Br2 (bromine gas).
8. Iodine (I)
- Forms 1 covalent bond with other atoms, typically with hydrogen, carbon, or other iodine atoms.
- Examples: HI (hydrogen iodide), CI4 (carbon tetraiodide), I2 (iodine gas).
Importance of Covalent Bonds

Covalent bonds play a crucial role in the formation of molecules and compounds. They determine the properties and behavior of substances, including their boiling and melting points, solubility, and reactivity. Understanding covalent bonds is essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Applications of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Materials science: Covalent bonds are used to create strong and durable materials, such as plastics and fibers.
- Biology: Covalent bonds are essential in the formation of biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA.
- Chemistry: Covalent bonds are used to synthesize compounds and to understand the properties and behavior of substances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, covalent bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding the essential covalent bonds formed by each element is crucial in various fields. By recognizing the factors that influence covalent bond formation and the importance of these bonds, we can better understand the properties and behavior of substances. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of covalent bonds and their significance in the world of chemistry.
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
What factors influence covalent bond formation?
+Electronegativity, valence electrons, atomic size, and bond energy are the factors that influence covalent bond formation.
Why are covalent bonds important?
+Covalent bonds determine the properties and behavior of substances, including their boiling and melting points, solubility, and reactivity.