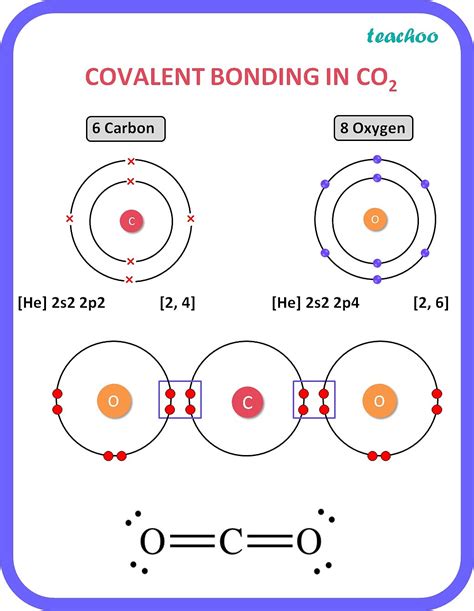
Carbon's unique ability to form a wide variety of compounds is due to its remarkable bonding capacity. One of the most fascinating aspects of carbon chemistry is its ability to form covalent bonds with other atoms. But have you ever wondered how many covalent bonds carbon can form? In this article, we'll delve into the world of carbon chemistry and explore the bonding capacity of this incredible element.
Carbon's Electronic Configuration

To understand carbon's bonding capacity, we need to look at its electronic configuration. Carbon has an atomic number of 6, which means it has 6 electrons in its atomic orbitals. The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p². This configuration indicates that carbon has 4 valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost energy level.
Tetravalency of Carbon

Carbon's 4 valence electrons are responsible for its tetravalency, which means it can form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms. This unique property allows carbon to form a wide variety of compounds, from simple molecules like methane (CH₄) to complex biomolecules like proteins and DNA.
How Carbon Forms Covalent Bonds
Carbon forms covalent bonds through a process called orbital hybridization. In this process, the 2s and 2p orbitals of carbon are mixed to form 4 equivalent sp³ hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are oriented in a tetrahedral shape, which allows carbon to form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms.
Types of Covalent Bonds Formed by Carbon

Carbon can form several types of covalent bonds, including:
- Sigma (σ) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals along the bond axis. Sigma bonds are typically strong and rigid.
- Pi (π) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals above and below the bond axis. Pi bonds are typically weaker than sigma bonds and are responsible for the formation of double and triple bonds.
Examples of Carbon's Bonding Capacity
- Methane (CH₄): In methane, carbon forms 4 covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms, resulting in a stable and symmetrical molecule.
- Ethene (C₂H₄): In ethene, carbon forms 3 covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms and 1 covalent bond with another carbon atom, resulting in a molecule with a double bond.
- Benzene (C₆H₆): In benzene, carbon forms 3 covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms and 3 covalent bonds with other carbon atoms, resulting in a molecule with a planar ring structure.
Carbon's Ability to Form Multiple Bonds

Carbon's ability to form multiple bonds is another aspect of its bonding capacity. Carbon can form double and triple bonds with other atoms, which are stronger than single bonds. These multiple bonds are responsible for the formation of complex molecules like alkenes and alkynes.
Examples of Carbon's Multiple Bonds
- Ethyne (C₂H₂): In ethyne, carbon forms a triple bond with another carbon atom, resulting in a molecule with a linear structure.
- Butadiene (C₄H₆): In butadiene, carbon forms a double bond with another carbon atom, resulting in a molecule with a conjugated system.
Carbon's Bonding Capacity in Biological Molecules

Carbon's bonding capacity plays a crucial role in the formation of biological molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. These molecules are composed of complex networks of carbon atoms bonded to other atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Examples of Carbon's Bonding Capacity in Biological Molecules
- Proteins: In proteins, carbon forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms, nitrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms, resulting in a complex 3D structure.
- DNA: In DNA, carbon forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms, nitrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms, resulting in a double-stranded helix structure.
In conclusion, carbon's bonding capacity is a remarkable property that allows it to form a wide variety of compounds, from simple molecules to complex biological molecules. Its ability to form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms makes it an essential element for life on Earth.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of carbon's bonding capacity. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form?
+Carbon can form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms.
What is the electronic configuration of carbon?
+The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p².
What is the significance of carbon's bonding capacity in biological molecules?
+Carbon's bonding capacity plays a crucial role in the formation of complex biological molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.