Bromine is a member of the halogen family, a group of highly reactive nonmetals that are known for their ability to readily form bonds with other elements. As a highly reactive element, bromine's bonding capacity is a topic of great interest in the field of chemistry. In this article, we will delve into the world of bromine chemistry and explore the various aspects of its bonding capacity.
Understanding Bromine's Atomic Structure
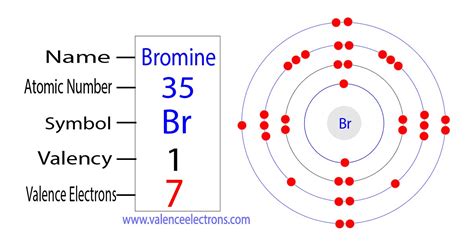
To understand how many bonds bromine can form, we need to first examine its atomic structure. Bromine is an element with the atomic number 35 and the atomic symbol Br. Its atomic structure consists of a nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons, with seven electrons in its outermost energy level. This electronic configuration is characteristic of the halogen family, and it plays a crucial role in determining bromine's bonding capacity.

Bromine's Valence Electrons
The number of valence electrons in an atom is a key factor in determining its bonding capacity. Valence electrons are the electrons in an atom's outermost energy level, and they play a crucial role in forming chemical bonds. In the case of bromine, it has seven valence electrons, which is one short of the full outer energy level that is characteristic of the noble gases. This means that bromine has a strong tendency to gain one electron to complete its outer energy level and achieve a stable electronic configuration.
How Many Bonds Can Bromine Form?
Bromine's bonding capacity is determined by its ability to form covalent bonds with other elements. Covalent bonds are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. In the case of bromine, it can form a maximum of four covalent bonds with other elements. This is because bromine has seven valence electrons, and it can form four single covalent bonds by sharing one pair of electrons with each of four other atoms.

Types of Bonds Formed by Bromine
Bromine can form a variety of bonds with other elements, including covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds. Covalent bonds are the most common type of bond formed by bromine, and they are typically formed with other nonmetals such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon. Ionic bonds are formed when bromine reacts with highly electropositive metals, resulting in the transfer of electrons and the formation of ions. Metallic bonds are formed when bromine reacts with other metals, resulting in the formation of a metal alloy.
Factors Affecting Bromine's Bonding Capacity
Several factors can affect bromine's bonding capacity, including its electronegativity, ionization energy, and electron affinity. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons, and bromine has a relatively high electronegativity value of 2.96. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, and bromine has a relatively high ionization energy value of 1140 kJ/mol. Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron is added to an atom, and bromine has a relatively high electron affinity value of 324 kJ/mol.

Practical Applications of Bromine's Bonding Capacity
Bromine's bonding capacity has a wide range of practical applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and water treatment. In pharmaceuticals, bromine is used as a disinfectant and as an intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs. In agriculture, bromine is used as a fumigant to control pests and diseases. In water treatment, bromine is used as a disinfectant to kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bromine's bonding capacity is a complex and multifaceted topic that is influenced by a variety of factors, including its atomic structure, valence electrons, and electronegativity. By understanding how many bonds bromine can form and the types of bonds it can form, we can better appreciate its importance in various industrial applications.
Stay Informed and Engaged!
We hope you found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. We also invite you to explore other articles on our website to learn more about the fascinating world of chemistry.
What is the atomic number of bromine?
+The atomic number of bromine is 35.
How many valence electrons does bromine have?
+Bromine has seven valence electrons.
What is the electronegativity value of bromine?
+The electronegativity value of bromine is 2.96.