Fluorine, being the most electronegative element in the periodic table, has a unique ability to form bonds with other elements. Its small size and high electronegativity make it an excellent candidate for forming strong covalent bonds. But, have you ever wondered how many bonds fluorine can form at most?

In this article, we'll delve into the world of fluorine and explore its bonding capabilities. We'll discuss the different types of bonds that fluorine can form, its limitations, and some interesting examples of compounds that showcase its unique bonding properties.
Understanding Fluorine's Bonding Capabilities
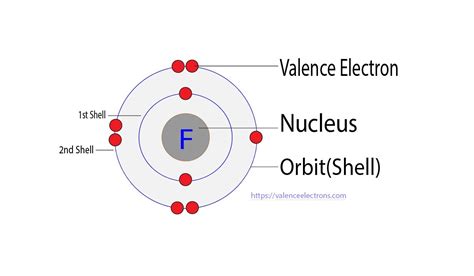
Fluorine, with its atomic number 9, has seven valence electrons in its outermost energy level. According to the octet rule, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level with eight electrons. Fluorine, being highly electronegative, readily forms covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other atoms.
In general, fluorine can form one, two, or three bonds with other atoms, depending on the type of compound being formed. Let's explore each of these bonding possibilities in more detail:
Single Bonds (1 Bond)
Fluorine can form single covalent bonds with other elements, such as hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. In these compounds, fluorine shares one pair of electrons with the other atom, resulting in a strong and stable bond. Examples of such compounds include hydrogen fluoride (HF), fluoromethane (CH3F), and fluoramine (NH2F).
Double Bonds (2 Bonds)
Fluorine can also form double covalent bonds with certain elements, such as carbon and oxygen. In these compounds, fluorine shares two pairs of electrons with the other atom, resulting in a stronger and more stable bond. Examples of such compounds include carbon dioxide (CO2), where fluorine is not directly involved, but fluorinated analogs like carbonyl fluoride (COF2) do exist.
Triple Bonds (3 Bonds)
In some rare cases, fluorine can form triple covalent bonds with certain elements, such as nitrogen and carbon. In these compounds, fluorine shares three pairs of electrons with the other atom, resulting in an extremely strong and stable bond. Examples of such compounds include nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) and trifluoromethyl radical (CF3).

Limitations of Fluorine's Bonding Capabilities
While fluorine can form multiple bonds with other elements, there are some limitations to its bonding capabilities. For example:
- Fluorine cannot form more than three bonds with another atom, due to its limited number of valence electrons.
- Fluorine's high electronegativity makes it difficult for it to form bonds with other highly electronegative elements, such as oxygen and nitrogen.
- Fluorine's small size makes it challenging to form bonds with large atoms or molecules.
Interesting Examples of Fluorine's Bonding Properties
Fluorine's unique bonding properties make it an interesting element to study. Here are some examples of compounds that showcase its bonding capabilities:
- Teflon (PTFE): A polymer composed of fluorine and carbon atoms, known for its non-stick properties.
- Fluoropolymers: A class of polymers that contain fluorine and other elements, used in a wide range of applications, from medical devices to cookware.
- Fluorinated gases: A class of gases that contain fluorine, used as refrigerants, propellants, and solvents.

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, fluorine's bonding capabilities are truly unique and fascinating. Its ability to form single, double, and triple bonds with other elements makes it an essential element in many industrial and commercial applications.
While fluorine's bonding capabilities are impressive, it's essential to remember its limitations. By understanding these limitations, scientists and engineers can design and develop new compounds and materials that take advantage of fluorine's unique properties.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of fluorine's bonding capabilities and its importance in the world of chemistry.
What is the maximum number of bonds fluorine can form?
+Fluorine can form a maximum of three bonds with another atom.
What is the most common type of bond fluorine forms?
+The most common type of bond fluorine forms is a single covalent bond.
What is an example of a compound that contains fluorine and exhibits unique bonding properties?
+Teflon (PTFE) is a polymer composed of fluorine and carbon atoms, known for its non-stick properties.