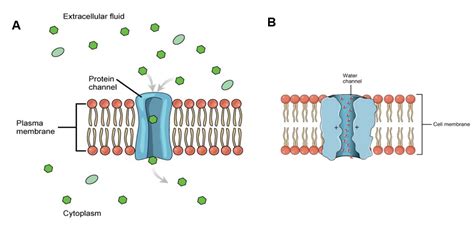
Cells are the basic units of life, and their membranes play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a lipid bilayer that separates the interior of the cell from its external environment. It is semi-permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while keeping others out. To facilitate the transport of molecules across the plasma membrane, cells have developed various channels and transport mechanisms. In this article, we will discuss seven channels that form across the plasma membrane, their functions, and importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Ion Channels Across the Plasma Membrane
Ion channels are a type of channel that forms across the plasma membrane, allowing ions to pass through. These channels are essential for maintaining the electrical properties of the cell and regulating the concentration of ions within the cell.

1. Potassium Channels
Potassium channels are a type of ion channel that allows potassium ions (K+) to pass through the plasma membrane. These channels are essential for maintaining the resting membrane potential of the cell and regulating the concentration of potassium ions within the cell.
2. Sodium Channels
Sodium channels are another type of ion channel that allows sodium ions (Na+) to pass through the plasma membrane. These channels are essential for generating action potentials in neurons and muscle cells.
3. Calcium Channels
Calcium channels are a type of ion channel that allows calcium ions (Ca2+) to pass through the plasma membrane. These channels are essential for regulating muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and hormone secretion.
Other Channels Across the Plasma Membrane
In addition to ion channels, there are other types of channels that form across the plasma membrane, allowing molecules to pass through.

4. Aquaporins
Aquaporins are a type of channel that allows water molecules (H2O) to pass through the plasma membrane. These channels are essential for regulating water transport across the cell membrane and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
5. Gap Junction Channels
Gap junction channels are a type of channel that allows molecules to pass directly from one cell to another. These channels are essential for coordinating cellular activities, such as muscle contraction and neuronal signaling.
6. Pore-Forming Toxins
Pore-forming toxins are a type of channel that forms across the plasma membrane, allowing ions and molecules to pass through. These channels are produced by certain bacteria and are essential for their pathogenicity.
7. ABC Transporter Channels
ABC transporter channels are a type of channel that uses energy to transport molecules across the plasma membrane. These channels are essential for regulating the concentration of molecules within the cell and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Importance of Channels Across the Plasma Membrane
Channels across the plasma membrane are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. They regulate the concentration of ions and molecules within the cell, facilitate the transport of molecules across the cell membrane, and coordinate cellular activities.

In conclusion, channels across the plasma membrane are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. The seven channels discussed in this article, including ion channels, aquaporins, gap junction channels, pore-forming toxins, and ABC transporter channels, play critical roles in regulating the concentration of ions and molecules within the cell, facilitating the transport of molecules across the cell membrane, and coordinating cellular activities. Understanding the structure and function of these channels is crucial for developing new treatments for various diseases and disorders.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the channels that form across the plasma membrane. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is the main function of ion channels across the plasma membrane?
+The main function of ion channels across the plasma membrane is to regulate the concentration of ions within the cell and maintain the electrical properties of the cell.
What is the role of aquaporins in cellular homeostasis?
+Aquaporins play a crucial role in regulating water transport across the cell membrane and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
What is the function of gap junction channels?
+Gap junction channels allow molecules to pass directly from one cell to another, coordinating cellular activities such as muscle contraction and neuronal signaling.