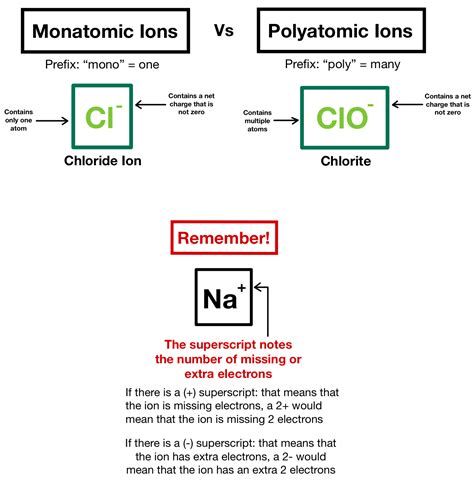
Monatomic ions are atoms that have gained or lost electrons to form ions with a single charge. The formation of monatomic ions is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding how they form is crucial for understanding various chemical reactions and processes. In this article, we will explore three ways monatomic ions form, including the gain or loss of electrons, the formation of ions through chemical reactions, and the formation of ions through physical processes.
Ion Formation through Electron Gain or Loss

One of the primary ways monatomic ions form is through the gain or loss of electrons. When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion with a single charge. The number of electrons gained or lost determines the charge of the ion. For example, when a sodium atom loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged sodium ion (Na+). Similarly, when a chlorine atom gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-).
This process of electron gain or loss is known as ionization. Ionization can occur through various means, including thermal energy, light, or chemical reactions. When an atom is ionized, it can either gain or lose electrons, resulting in the formation of a monatomic ion.
Electron Gain
Electron gain occurs when an atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion. This process is also known as electron capture. When an atom gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged ion with a single charge. For example, when a fluorine atom gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged fluoride ion (F-).
Electron Loss
Electron loss occurs when an atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion. This process is also known as electron emission. When an atom loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged ion with a single charge. For example, when a lithium atom loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged lithium ion (Li+).
Ion Formation through Chemical Reactions

Monatomic ions can also form through chemical reactions. Chemical reactions involve the interaction of atoms or molecules, resulting in the formation of new compounds or ions. When a chemical reaction occurs, the atoms or molecules involved can gain or lose electrons, resulting in the formation of monatomic ions.
For example, when sodium metal reacts with chlorine gas, the sodium atoms lose electrons to form positively charged sodium ions (Na+), while the chlorine atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged chloride ions (Cl-). This reaction results in the formation of sodium chloride (NaCl), also known as table salt.
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are several types of chemical reactions that can result in the formation of monatomic ions, including:
- Synthesis reactions: These reactions involve the combination of two or more atoms or molecules to form a new compound.
- Decomposition reactions: These reactions involve the breakdown of a compound into its constituent atoms or molecules.
- Replacement reactions: These reactions involve the replacement of one atom or molecule with another.
Ion Formation through Physical Processes

Monatomic ions can also form through physical processes, such as radiation or high-energy collisions. When an atom is exposed to radiation or high-energy collisions, it can gain or lose electrons, resulting in the formation of a monatomic ion.
For example, when an atom is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, it can gain energy and lose an electron, resulting in the formation of a positively charged ion. Similarly, when an atom is exposed to high-energy collisions, it can gain or lose electrons, resulting in the formation of a monatomic ion.
Types of Physical Processes
There are several types of physical processes that can result in the formation of monatomic ions, including:
- Radiation: This includes exposure to UV radiation, X-rays, or other forms of electromagnetic radiation.
- High-energy collisions: This includes collisions with other atoms or molecules, or with high-energy particles such as electrons or protons.
FAQ Section:
What is a monatomic ion?
+A monatomic ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons to form an ion with a single charge.
How do monatomic ions form?
+Monatomic ions can form through the gain or loss of electrons, chemical reactions, or physical processes such as radiation or high-energy collisions.
What is the difference between electron gain and electron loss?
+Electron gain occurs when an atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion, while electron loss occurs when an atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion.
In conclusion, monatomic ions can form through various means, including the gain or loss of electrons, chemical reactions, and physical processes. Understanding how monatomic ions form is crucial for understanding various chemical reactions and processes. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the three ways monatomic ions form. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.