Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Forming The Initiation Complex

Transcription is a fundamental process in molecular biology where genetic information is transcribed from DNA into RNA. In eukaryotic cells, this process is highly regulated and involves a complex interplay of various transcription factors. These proteins play a crucial role in recruiting RNA polymerase, the enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA, to specific gene promoters.
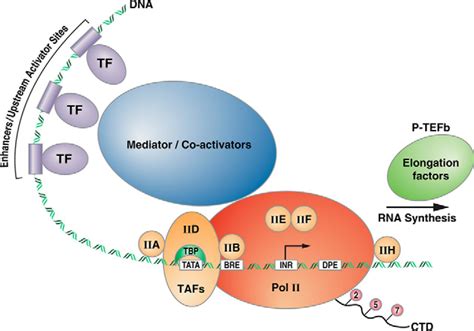
One of the most critical steps in eukaryotic transcription is the formation of the pre-initiation complex (PIC). This complex is composed of multiple transcription factors that come together to facilitate the recruitment of RNA polymerase II to the promoter region of a gene. In this article, we will delve into the world of eukaryotic transcription factors and explore the intricacies of PIC formation.
Understanding Transcription Factors
Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences, known as cis-elements, near the promoter region of a gene. These proteins can either stimulate or inhibit transcription, depending on their function and the context in which they are acting. Eukaryotic transcription factors are highly diverse, with over 1,500 known factors in humans alone.
Transcription factors can be broadly classified into two categories: general transcription factors (GTFs) and transcriptional activators/repressors. GTFs are essential for the recruitment of RNA polymerase II and the formation of the PIC, while transcriptional activators/repressors regulate the activity of GTFs and RNA polymerase II.
The Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC)

The pre-initiation complex is a critical assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II that forms at the promoter region of a gene. The PIC is composed of multiple subunits, including:
- TFIID: A complex of TATA-binding protein (TBP) and TBP-associated factors (TAFs)
- TFIIA: A protein complex that binds to the TBP and TAFs
- TFIIB: A protein that recruits RNA polymerase II to the promoter
- TFIIF: A protein complex that helps to recruit RNA polymerase II and stabilizes the PIC
- TFIIH: A protein complex that has helicase and kinase activities
- RNA polymerase II: The enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA
The formation of the PIC is a highly regulated process that involves a series of protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. The assembly of the PIC is initiated by the binding of TFIID to the TATA box, a specific DNA sequence located near the promoter region of a gene.
Steps Involved in PIC Formation
The formation of the PIC involves a series of steps, including:
- TFIID binding to the TATA box
- Recruitment of TFIIA to the TBP-TAF complex
- Binding of TFIIB to the TBP-TAF-TFIIA complex
- Recruitment of TFIIF to the complex
- Binding of TFIIH to the complex
- Recruitment of RNA polymerase II to the complex
Each of these steps is highly regulated and involves specific protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions.
Regulation of PIC Formation

The formation of the PIC is regulated by a variety of mechanisms, including:
- Transcriptional activators/repressors: These proteins can either stimulate or inhibit the activity of GTFs and RNA polymerase II.
- Chromatin remodeling: The structure of chromatin can affect the accessibility of transcription factors to the promoter region.
- Histone modification: Histone modifications can affect the binding of transcription factors to the promoter region.
- DNA methylation: DNA methylation can affect the binding of transcription factors to the promoter region.
These regulatory mechanisms ensure that gene expression is tightly controlled and responsive to changing cellular conditions.
Consequences of Dysregulation
Dysregulation of PIC formation can have significant consequences, including:
- Cancer: Dysregulation of transcription factors and PIC formation has been implicated in the development of various cancers.
- Developmental disorders: Dysregulation of transcription factors and PIC formation has been implicated in the development of various developmental disorders.
- Neurological disorders: Dysregulation of transcription factors and PIC formation has been implicated in the development of various neurological disorders.
In conclusion, the formation of the pre-initiation complex is a critical step in eukaryotic transcription. Understanding the intricacies of PIC formation and regulation can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of gene expression and the development of various diseases.
What is the role of transcription factors in PIC formation?
+Transcription factors play a crucial role in recruiting RNA polymerase II to the promoter region of a gene and facilitating the formation of the pre-initiation complex.
What is the composition of the PIC?
+The PIC is composed of multiple subunits, including TFIID, TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIF, TFIIH, and RNA polymerase II.
What are the consequences of dysregulation of PIC formation?
+Dysregulation of PIC formation can have significant consequences, including cancer, developmental disorders, and neurological disorders.