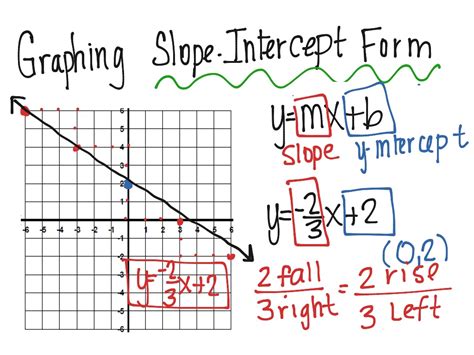
Graphing slope-intercept form is an essential skill in algebra and mathematics, allowing you to visualize and analyze linear equations. Slope-intercept form, denoted as y = mx + b, represents a linear equation where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Mastering this concept enables you to understand how to graph lines, identify their characteristics, and solve problems in various fields. In this article, we will explore seven tips to help you master graphing slope-intercept form.

Understanding the Basics
To graph a slope-intercept form equation, you need to understand the components of the equation. The slope (m) represents the rate of change between the y-coordinate and the x-coordinate. The y-intercept (b) is the point where the line intersects the y-axis. When graphing, you can start by plotting the y-intercept and then using the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line.
Tip 1: Plotting the Y-Intercept
The y-intercept is the easiest part of the equation to plot. It's the point where the line crosses the y-axis. To plot the y-intercept, locate the value of b on the y-axis and mark a point. This point will serve as a reference for graphing the rest of the line.

Using the Slope to Graph the Line
The slope of the line determines its direction and steepness. A positive slope indicates a line that slopes upward from left to right, while a negative slope indicates a line that slopes downward from left to right. A slope of zero represents a horizontal line, and an undefined slope represents a vertical line.
Tip 2: Determining the Slope
To determine the slope, look at the coefficient of x (m). If m is positive, the line slopes upward. If m is negative, the line slopes downward. If m is zero, the line is horizontal. If m is undefined, the line is vertical.

Graphing the Line
With the y-intercept plotted and the slope determined, you can start graphing the line. Use the slope to find a second point on the line. From the y-intercept, move up or down by the slope value and then move right or left by one unit.
Tip 3: Finding a Second Point
To find a second point on the line, start at the y-intercept and move up or down by the slope value. Then, move right or left by one unit. This will give you a second point on the line. For example, if the slope is 2 and the y-intercept is (0, 3), start at (0, 3) and move up 2 units to (0, 5). Then, move right one unit to (1, 5).

Graphing Multiple Points
To create a more accurate graph, find multiple points on the line. Use the slope to find additional points, and then draw a line through all the points.
Tip 4: Finding Multiple Points
To find multiple points, use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line. From each point, move up or down by the slope value and then move right or left by one unit. For example, if the slope is 2 and the y-intercept is (0, 3), start at (0, 3) and move up 2 units to (0, 5). Then, move right one unit to (1, 5). From (1, 5), move up 2 units to (1, 7) and then move right one unit to (2, 7).

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When graphing slope-intercept form, there are several common mistakes to avoid. Make sure to plot the y-intercept correctly and use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line. Also, avoid confusing the slope with the y-intercept.
Tip 5: Avoiding Common Mistakes
To avoid common mistakes, double-check your work. Make sure to plot the y-intercept correctly and use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line. Also, avoid confusing the slope with the y-intercept. For example, if the equation is y = 2x + 3, the slope is 2, and the y-intercept is (0, 3). Make sure to plot the y-intercept at (0, 3) and use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line.

Real-World Applications
Graphing slope-intercept form has several real-world applications. It can be used to model population growth, financial trends, and scientific data. By understanding how to graph slope-intercept form, you can analyze and interpret data in various fields.
Tip 6: Real-World Applications
To apply graphing slope-intercept form to real-world problems, identify the slope and y-intercept of the equation. Use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line, and then use the y-intercept to identify the starting point. For example, if a company's profit is modeled by the equation y = 2x + 500, the slope is 2, and the y-intercept is (0, 500). This means that the company's profit starts at $500 and increases by $2 for every unit sold.

Practice Makes Perfect
To master graphing slope-intercept form, practice is key. Start by graphing simple equations and gradually move on to more complex ones. Use online resources or graphing calculators to check your work and build your confidence.
Tip 7: Practice Makes Perfect
To practice graphing slope-intercept form, start by graphing simple equations such as y = x + 1 or y = 2x - 3. Gradually move on to more complex equations such as y = 3x^2 + 2x - 1. Use online resources or graphing calculators to check your work and build your confidence. You can also use worksheets or online quizzes to test your skills and identify areas for improvement.

Now that you've mastered the seven tips for graphing slope-intercept form, it's time to put your skills to the test. Try graphing different equations and analyzing their characteristics. Remember to practice regularly and use online resources to build your confidence. With time and effort, you'll become a pro at graphing slope-intercept form and be able to tackle more complex math problems with ease.
What is slope-intercept form?
+Slope-intercept form is a way of representing a linear equation in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do I graph a slope-intercept form equation?
+To graph a slope-intercept form equation, start by plotting the y-intercept. Then, use the slope to determine the direction and steepness of the line. Find multiple points on the line and draw a line through all the points.
What is the difference between the slope and the y-intercept?
+The slope represents the rate of change between the y-coordinate and the x-coordinate, while the y-intercept is the point where the line intersects the y-axis.