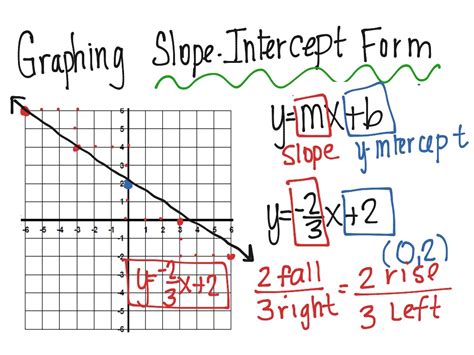
Understanding the concept of slope intercept form is a crucial aspect of graphing and analyzing linear equations. The slope intercept form, often denoted as y = mx + b, is a fundamental concept in algebra and geometry. Here, m represents the slope of the line, and b represents the y-intercept. Mastering this concept can help you solve problems efficiently and accurately.
The importance of slope intercept form lies in its ability to provide a clear and concise way to represent linear equations. It allows us to understand the behavior of a line, including its steepness and the point at which it intersects the y-axis. By understanding how to graph slope intercept form equations, you can better analyze and solve problems in various mathematical and real-world contexts.
From basic algebra to advanced calculus, the slope intercept form plays a critical role in mathematical problem-solving. It is essential to grasp this concept to build a strong foundation in mathematics and to tackle more complex problems with confidence. In this article, we will explore five tips to help you master slope intercept form graphing.
Tip 1: Understand the Components of Slope Intercept Form

The slope intercept form equation, y = mx + b, consists of two primary components: the slope (m) and the y-intercept (b). The slope represents the steepness of the line, while the y-intercept represents the point at which the line intersects the y-axis.
To graph a slope intercept form equation, it is essential to understand the roles of these two components. The slope determines the direction and steepness of the line, while the y-intercept provides the starting point for graphing the line.
Understanding the Slope (m)
The slope of a line is a measure of how steep it is. A positive slope indicates a line that rises from left to right, while a negative slope indicates a line that falls from left to right. A slope of zero represents a horizontal line, while an undefined slope represents a vertical line.
Understanding the Y-Intercept (b)
The y-intercept is the point at which the line intersects the y-axis. It represents the starting point for graphing the line. A positive y-intercept indicates that the line intersects the y-axis above the origin, while a negative y-intercept indicates that the line intersects the y-axis below the origin.
Tip 2: Plot the Y-Intercept

Once you have identified the y-intercept, plot it on the graph. This will provide the starting point for graphing the line. If the y-intercept is positive, plot the point above the origin. If the y-intercept is negative, plot the point below the origin.
Plotting the y-intercept is a crucial step in graphing slope intercept form equations. It provides the foundation for drawing the line and ensures that the line intersects the y-axis at the correct point.
Tip 3: Use the Slope to Draw the Line

After plotting the y-intercept, use the slope to draw the line. The slope will determine the direction and steepness of the line. If the slope is positive, draw the line rising from left to right. If the slope is negative, draw the line falling from left to right.
To use the slope to draw the line, you can use a technique called "rise over run." This involves drawing a vertical line (rise) and then a horizontal line (run) to create a right triangle. The ratio of the rise to the run is equal to the slope.
Tip 4: Check Your Work

Once you have graphed the line, check your work to ensure that it is accurate. You can do this by plugging in a few points into the equation to see if they lie on the line.
Checking your work is an essential step in graphing slope intercept form equations. It helps to ensure that your graph is accurate and provides a way to catch any mistakes.
Tip 5: Practice, Practice, Practice

Finally, practice is key to mastering slope intercept form graphing. The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with graphing slope intercept form equations.
To practice, try graphing different slope intercept form equations. Start with simple equations and gradually move on to more complex ones. You can also use online resources or graphing calculators to practice graphing slope intercept form equations.
In conclusion, mastering slope intercept form graphing requires a combination of understanding the components of the equation, plotting the y-intercept, using the slope to draw the line, checking your work, and practicing. By following these tips, you can become proficient in graphing slope intercept form equations and build a strong foundation in mathematics.
What is the slope intercept form of a linear equation?
+The slope intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do I plot the y-intercept on a graph?
+To plot the y-intercept, identify the point where the line intersects the y-axis. If the y-intercept is positive, plot the point above the origin. If the y-intercept is negative, plot the point below the origin.
What is the role of the slope in graphing a slope intercept form equation?
+The slope determines the direction and steepness of the line. A positive slope indicates a line that rises from left to right, while a negative slope indicates a line that falls from left to right.