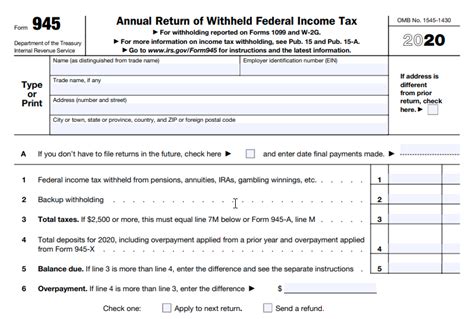
The Form 945, also known as the Annual Return of Withheld Federal Income Tax, is a crucial document that employers must file with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to report federal income tax withheld from nonpayroll payments. Filing this form accurately and on time is essential to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with tax laws.
Understanding the Importance of Form 945

Form 945 is used to report federal income tax withheld from various types of payments, including backup withholding, withholding on pensions and annuities, and withholding on certain government payments. Employers who have withheld federal income tax from these types of payments during the calendar year must file Form 945 by January 31st of the following year.
Who Needs to File Form 945?
Not all employers are required to file Form 945. Generally, employers who have withheld federal income tax from nonpayroll payments, such as:
- Backup withholding
- Withholding on pensions and annuities
- Withholding on certain government payments
must file Form 945.
Step-by-Step Filing Guide for Form 945

Filing Form 945 involves several steps, which are outlined below:
Step 1: Gather Required Information
Before starting the filing process, employers must gather the following information:
- Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Total amount of federal income tax withheld during the calendar year
- Total amount of nonpayroll payments subject to withholding
- Number of payees
Step 2: Complete Form 945
Employers must complete Form 945, which consists of three parts:
- Part 1: Annual Return of Withheld Federal Income Tax
- Part 2: Reconciliation of Income Tax Withheld
- Part 3: Summary of Federal Tax Liability
Employers must report the total amount of federal income tax withheld, the total amount of nonpayroll payments subject to withholding, and the number of payees.
Step 3: Report Federal Tax Liability
Employers must report their federal tax liability for the calendar year on Part 3 of Form 945.
Step 4: File Form 945
Employers must file Form 945 by January 31st of the following year. Employers can file the form electronically or by mail.
Electronic Filing Options for Form 945

Employers can file Form 945 electronically using the following options:
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- IRS Free File
- Tax preparation software
Electronic filing offers several benefits, including faster processing, reduced errors, and easier tracking.
Common Errors to Avoid When Filing Form 945

Employers must avoid common errors when filing Form 945, including:
- Inaccurate reporting of federal income tax withheld
- Failure to report all nonpayroll payments subject to withholding
- Incorrect calculation of federal tax liability
Employers can avoid these errors by carefully reviewing the form instructions and seeking professional help if needed.
Penalties for Late or Inaccurate Filing of Form 945

Employers who fail to file Form 945 on time or accurately may face penalties, including:
- Late filing penalty
- Late payment penalty
- Accuracy-related penalty
Employers can avoid these penalties by filing Form 945 accurately and on time.
Conclusion
Filing Form 945 is a critical task for employers who have withheld federal income tax from nonpayroll payments. By following the step-by-step guide outlined above, employers can ensure accurate and timely filing of Form 945. Employers must also be aware of common errors to avoid and penalties for late or inaccurate filing.
If you have any questions or concerns about filing Form 945, please leave a comment below or share this article with your colleagues.
What is the deadline for filing Form 945?
+The deadline for filing Form 945 is January 31st of the following year.
Who is required to file Form 945?
+Employers who have withheld federal income tax from nonpayroll payments, such as backup withholding, withholding on pensions and annuities, and withholding on certain government payments, are required to file Form 945.
What are the penalties for late or inaccurate filing of Form 945?
+Employers who fail to file Form 945 on time or accurately may face penalties, including late filing penalty, late payment penalty, and accuracy-related penalty.