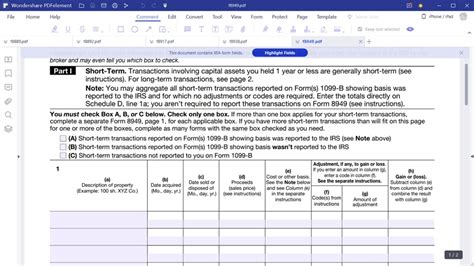
As the tax season approaches, many investors and taxpayers are preparing to file their returns. One crucial form for those who have bought or sold securities, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, is Form 8949. This form is used to report sales and other dispositions of capital assets, which are then carried over to Schedule D to calculate the capital gains or losses. Within Form 8949, Box F is particularly important as it deals with the codes for the type of transaction being reported. Understanding the nuances of Box F is essential for accurate reporting and avoiding potential IRS issues. Here are five essential facts about Form 8949 Box F that you should know.
Understanding the Basics of Form 8949
Before diving into the specifics of Box F, it's crucial to understand the purpose of Form 8949. This form is a critical component of your tax return if you have engaged in any investment activities during the tax year. Whether you've sold stocks, bonds, ETFs, or any other type of capital asset, you'll need to report these transactions. The form breaks down your sales and purchases into separate categories, making it easier to calculate your net capital gain or loss for the year.

The Role of Box F in Form 8949
Box F on Form 8949 is designated for entering a code that identifies the type of transaction being reported. This code is critical because it tells the IRS the nature of the sale or disposition. For example, if you sold securities, the code might indicate whether it was a short-term or long-term sale, which significantly impacts the tax implications.
Codes Used in Box F
The IRS has specified several codes that can be used in Box F, each representing a different type of transaction. For instance:
- Code A: Short-term transactions (those held for one year or less)
- Code B: Long-term transactions (those held for more than one year)
- Code C: Constructive sales of appreciated financial positions
- Code D: Wash sales disallowed
- Code E: Transactions reported on Form 1099-B showing basis reported to the IRS
- Code G: Sales reported on Form 1099-B with basis NOT reported to the IRS
Using the correct code in Box F is vital to ensure that your transactions are reported accurately and that you're taking advantage of the most favorable tax treatment available.
Consequences of Incorrect Reporting
Incorrectly filling out Box F or using the wrong code can lead to errors in your tax return, which might trigger an IRS audit. Moreover, it could result in you paying more in taxes than you owe if you fail to claim the correct long-term or short-term capital gain treatment. On the other hand, intentionally misreporting transactions to avoid taxes can lead to severe penalties, including fines and interest on the amount owed.

Best Practices for Filling Out Box F
To ensure accuracy when filling out Box F, it's essential to carefully review the instructions provided with Form 8949. Additionally, keep detailed records of all your investment transactions, including dates of purchase and sale, the type of asset, and the gain or loss. If you're unsure about how to report a transaction or which code to use, consider consulting a tax professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation and ensure that your tax return is accurate and compliant with IRS regulations.
Technological Solutions for Simplifying Tax Reporting
With the advancement of technology, several software programs and online tools have been developed to simplify the process of filling out tax forms, including Form 8949. These tools can guide you through the reporting process, help you choose the correct codes for Box F, and even import transaction data from your brokerage accounts. While technology can significantly reduce the complexity of tax reporting, it's still important to understand the basics and ensure that the information being reported is accurate.
In conclusion, Form 8949 Box F plays a critical role in accurately reporting capital asset transactions on your tax return. Understanding the codes used in Box F and their implications is essential for avoiding potential issues with the IRS. By staying informed and possibly leveraging technological solutions, you can navigate the complexities of tax reporting with confidence.
What is Form 8949 used for?
+Form 8949 is used to report sales and other dispositions of capital assets, which are then carried over to Schedule D to calculate the capital gains or losses.
What is the purpose of Box F on Form 8949?
+What are the consequences of incorrectly filling out Box F?
+Incorrectly filling out Box F can lead to errors in your tax return, potentially triggering an IRS audit, and may result in paying more in taxes than owed or severe penalties for intentional misreporting.