As a fiduciary, navigating the complexities of Form 1041, also known as the U.S. Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts, can be a daunting task. One of the most critical components of this form is Schedule D, which reports the capital gains and losses from the sale of assets. Mastering Form 1041 Schedule D is essential to ensure accurate reporting and minimize potential errors or penalties. In this article, we will provide five valuable tips to help you master Form 1041 Schedule D and streamline your tax preparation process.
Understanding the Basics of Form 1041 Schedule D
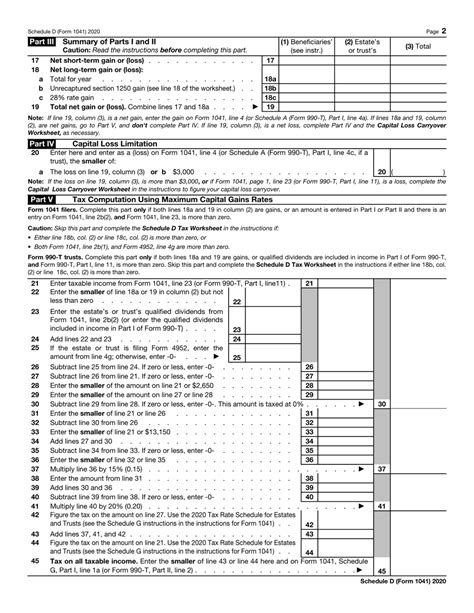
Before diving into the tips, it's essential to understand the basics of Form 1041 Schedule D. This schedule is used to report the capital gains and losses from the sale of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment properties. The schedule is divided into two parts: Part I, which reports the short-term capital gains and losses, and Part II, which reports the long-term capital gains and losses.

Tip 1: Identify the Correct Filing Status
The first step in mastering Form 1041 Schedule D is to identify the correct filing status. As a fiduciary, you will need to determine whether the estate or trust is filing as a single entity or as a grantor trust. This determination will impact the way you report capital gains and losses on Schedule D.
To determine the correct filing status, you will need to review the trust agreement or will to identify the grantor or beneficiaries. If the grantor is still alive, the trust will likely be treated as a grantor trust, and the grantor's tax identification number will be used. If the grantor has passed away, the trust will be treated as a separate entity, and a separate tax identification number will be required.
Tip 2: Gather Accurate Information
To accurately complete Form 1041 Schedule D, you will need to gather accurate information about the sale of assets. This includes:
- Date of sale
- Proceeds from the sale
- Basis of the asset
- Holding period
- Any commissions or fees associated with the sale
You can obtain this information from the following sources:
- Brokerage statements
- Real estate closing documents
- Appraisals
- Trust accounting records
It's essential to ensure that the information is accurate and complete, as errors can result in delays or penalties.
Tip 3: Calculate Capital Gains and Losses
Once you have gathered the necessary information, you will need to calculate the capital gains and losses. This involves determining the gain or loss from the sale of each asset and reporting it on Schedule D.
To calculate the gain or loss, you will need to subtract the basis from the proceeds. For example, if the proceeds from the sale of a stock are $10,000 and the basis is $5,000, the gain would be $5,000.
If the gain is short-term (held for one year or less), it will be reported on Part I of Schedule D. If the gain is long-term (held for more than one year), it will be reported on Part II of Schedule D.
Tip 4: Net Capital Gains and Losses
After calculating the gain or loss from each asset, you will need to net the capital gains and losses. This involves combining the gains and losses from all assets to determine the net gain or loss.
For example, if the estate has a gain of $5,000 from the sale of one stock and a loss of $3,000 from the sale of another stock, the net gain would be $2,000.
Tip 5: Report Capital Gains and Losses on Schedule D
Finally, you will need to report the net capital gains and losses on Schedule D. This involves completing the following sections:
- Part I: Short-term capital gains and losses
- Part II: Long-term capital gains and losses
- Part III: Netting of gains and losses
You will also need to complete Form 8949, which reports the sales and other dispositions of capital assets.

Conclusion: Mastering Form 1041 Schedule D
Mastering Form 1041 Schedule D requires attention to detail, accurate information, and a thorough understanding of the tax laws and regulations. By following these five tips, you can ensure accurate reporting and minimize potential errors or penalties.
As a fiduciary, it's essential to stay up-to-date on the latest tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid any potential issues. By taking the time to master Form 1041 Schedule D, you can provide better service to your clients and ensure that their tax returns are accurate and complete.
We encourage you to share your experiences and tips for mastering Form 1041 Schedule D in the comments below. Don't forget to share this article with your colleagues and friends who may benefit from this information.
What is Form 1041 Schedule D?
+Form 1041 Schedule D is used to report the capital gains and losses from the sale of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment properties.
What is the difference between Part I and Part II of Schedule D?
+Part I reports the short-term capital gains and losses, while Part II reports the long-term capital gains and losses.
How do I calculate the net capital gains and losses?
+You can calculate the net capital gains and losses by combining the gains and losses from all assets to determine the net gain or loss.