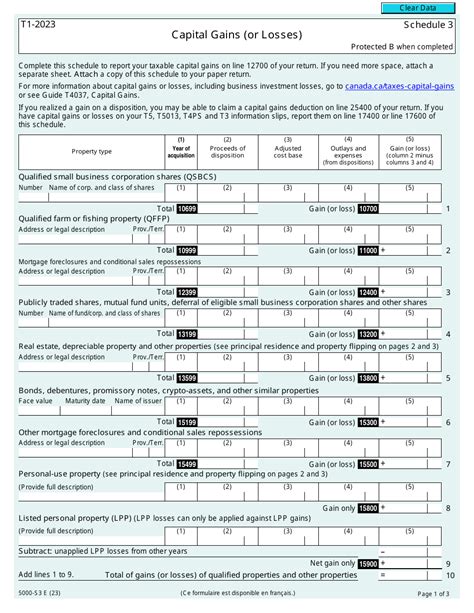
Federal tax forms can be overwhelming, especially for those who are new to filing taxes. One of the most important forms for investors is Schedule 3, which deals with capital gains and losses. In this article, we will delve into the world of Schedule 3 and explore what it entails, how to fill it out, and what you need to know to avoid any errors or penalties.
Capital gains are profits made from the sale of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investments. These gains are subject to taxation, and the amount of tax owed depends on the type of asset sold, the length of time it was held, and the taxpayer's income tax bracket. Schedule 3 is used to report these gains and losses to the IRS.
What is Schedule 3?

Schedule 3 is a supplemental form that is attached to the main tax return, Form 1040. It is used to report capital gains and losses from the sale of assets, as well as other income such as interest and dividends. The form is divided into several sections, each dealing with a specific type of income or expense.
Types of Capital Gains
There are two types of capital gains: short-term and long-term. Short-term gains are profits made from the sale of assets held for one year or less. These gains are taxed as ordinary income and are subject to the taxpayer's regular income tax rate. Long-term gains, on the other hand, are profits made from the sale of assets held for more than one year. These gains are taxed at a lower rate, typically 15% or 20%, depending on the taxpayer's income tax bracket.
How to Fill Out Schedule 3

Filling out Schedule 3 can be a bit complex, but it's essential to get it right to avoid any errors or penalties. Here are the steps to follow:
- Gather all necessary documents: You will need to gather all the necessary documents, including Form 1099-B, which shows the sale of securities, and Form 8949, which is used to report sales and other dispositions of capital assets.
- Identify the type of asset sold: Determine the type of asset sold, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Determine the gain or loss: Calculate the gain or loss from the sale of the asset. You can use Form 8949 to help you calculate the gain or loss.
- Complete Part I: Complete Part I of Schedule 3, which deals with short-term gains and losses.
- Complete Part II: Complete Part II of Schedule 3, which deals with long-term gains and losses.
- Complete Part III: Complete Part III of Schedule 3, which deals with other income and expenses.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When filling out Schedule 3, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
- Incorrectly reporting gains and losses: Make sure to report gains and losses correctly, as this can affect your tax liability.
- Failing to report all sales: Make sure to report all sales of assets, even if they result in a loss.
- Not keeping accurate records: Keep accurate records of all sales and purchases of assets, as this will help you to accurately complete Schedule 3.
Capital Gains Tax Rates

Capital gains tax rates vary depending on the taxpayer's income tax bracket and the length of time the asset was held. Here are the current capital gains tax rates:
- 0%: Taxpayers in the 10% and 12% income tax brackets pay 0% on long-term capital gains.
- 15%: Taxpayers in the 22%, 24%, 32%, and 35% income tax brackets pay 15% on long-term capital gains.
- 20%: Taxpayers in the 37% income tax bracket pay 20% on long-term capital gains.
Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
Here are some strategies to minimize capital gains tax:
- Hold assets for more than one year: Holding assets for more than one year can help to reduce capital gains tax, as long-term gains are taxed at a lower rate.
- Sell assets in a tax-loss year: Selling assets in a tax-loss year can help to reduce capital gains tax, as losses can be used to offset gains.
- Consider a tax-loss harvest: A tax-loss harvest involves selling assets that have declined in value to realize losses, which can be used to offset gains.
Conclusion

Schedule 3 is an essential form for investors, as it deals with capital gains and losses. By understanding how to fill out the form correctly and minimizing capital gains tax, taxpayers can save money and avoid any errors or penalties. Remember to keep accurate records, report all sales, and consider strategies to minimize capital gains tax.
What's Next?
We hope this article has helped you to understand Schedule 3 and capital gains tax. If you have any questions or comments, please let us know. Remember to share this article with others who may find it helpful.
FAQ Section:
What is Schedule 3?
+Schedule 3 is a supplemental form that is attached to the main tax return, Form 1040. It is used to report capital gains and losses from the sale of assets, as well as other income such as interest and dividends.
How do I fill out Schedule 3?
+To fill out Schedule 3, you will need to gather all necessary documents, including Form 1099-B and Form 8949. You will then need to identify the type of asset sold, determine the gain or loss, and complete Parts I, II, and III of the form.
What are the capital gains tax rates?
+Capital gains tax rates vary depending on the taxpayer's income tax bracket and the length of time the asset was held. The current capital gains tax rates are 0%, 15%, and 20%.