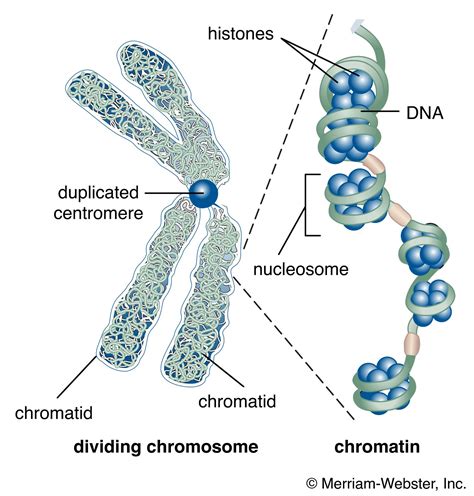
Cell division is a fundamental process in biology that allows living organisms to grow, reproduce, and repair tissues. During cell division, a crucial step occurs where chromatin, the complex of DNA and proteins, condenses into visible chromosomes. This process is essential for the proper segregation of genetic material into daughter cells. In this article, we will explore the importance of chromatin condensation, the mechanisms involved, and the stages of cell division where it occurs.

Importance of Chromatin Condensation
Chromatin condensation is a critical step in cell division, as it allows for the accurate separation of chromosomes into daughter cells. If chromatin fails to condense properly, it can lead to errors in chromosome segregation, resulting in genetic abnormalities and potentially causing diseases such as cancer. Moreover, chromatin condensation is necessary for the formation of a compact and organized chromosome structure, which facilitates the attachment of microtubules and the movement of chromosomes during cell division.
Consequences of Chromatin Condensation Failure
Failure of chromatin condensation can have severe consequences, including:
• Genetic instability: Chromatin condensation errors can lead to genetic mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, and aneuploidy (having an abnormal number of chromosomes). • Cellular defects: Defects in chromatin condensation can result in aberrant cell growth, differentiation, and survival. • Disease susceptibility: Chromatin condensation errors have been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and developmental abnormalities.
Mechanisms of Chromatin Condensation
Chromatin condensation is a complex process involving multiple molecular mechanisms. The following steps outline the key events:

Step 1: Chromatin Remodeling
Chromatin remodeling complexes, such as SWI/SNF and INO80, reorganize chromatin structure by moving nucleosomes (the basic units of chromatin) and creating a more compact and accessible chromatin environment.
Step 2: Histone Modification
Histone-modifying enzymes add various post-translational modifications to histone proteins, including phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation. These modifications alter chromatin structure and facilitate condensation.
Step 3: Condensin Complex Assembly
Condensin complexes, consisting of SMC (Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes) proteins and associated proteins, assemble on chromatin and initiate condensation.
Step 4: Chromatin Compaction
Condensin complexes and other chromatin-binding proteins, such as cohesin and topoisomerase II, work together to compact chromatin into visible chromosomes.
Stages of Cell Division Where Chromatin Condensation Occurs
Chromatin condensation occurs during the following stages of cell division:

Prophase
Chromatin condensation begins in prophase, where chromatin is condensed into visible chromosomes.
Metaphase
Chromatin condensation is completed in metaphase, where chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase
Chromatin remains condensed during anaphase, where sister chromatids are separated and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase
Chromatin decondenses in telophase, where chromosomes return to their interphase structure.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, chromatin condensation is a critical process in cell division that ensures the proper segregation of genetic material into daughter cells. Understanding the mechanisms and stages of chromatin condensation is essential for unraveling the complexities of cell division and addressing related diseases. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise molecular mechanisms of chromatin condensation and its regulation, which will ultimately contribute to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for diseases related to chromatin condensation errors.
What is chromatin condensation?
+Chromatin condensation is the process by which chromatin, the complex of DNA and proteins, is compacted into visible chromosomes during cell division.
Why is chromatin condensation important?
+Chromatin condensation is crucial for the accurate separation of chromosomes into daughter cells during cell division. Failure of chromatin condensation can lead to genetic abnormalities and diseases.
What are the consequences of chromatin condensation failure?
+Consequences of chromatin condensation failure include genetic instability, cellular defects, and disease susceptibility, such as cancer, neurological disorders, and developmental abnormalities.