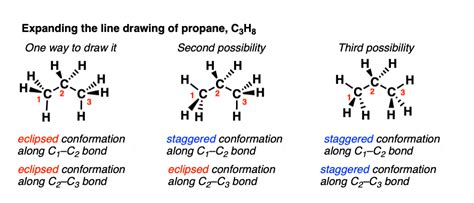
Propane is a simple hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C3H8, consisting of three carbon atoms bonded to eight hydrogen atoms. Despite its simplicity, propane can form isomers, which are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Isomers are an important concept in organic chemistry, as they can exhibit different physical and chemical properties. In this article, we will explore three ways propane can form isomers.
Structural Isomerism

One way propane can form isomers is through structural isomerism. Structural isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of their atoms. Propane can form two structural isomers: n-propane and isopropane. N-propane has a straight chain of three carbon atoms, while isopropane has a branched chain with a central carbon atom bonded to two methyl groups.
The structural isomers of propane have different physical properties, such as boiling points and densities. N-propane has a boiling point of -42.2°C, while isopropane has a boiling point of -11.7°C. This difference in boiling points is due to the different shapes of the molecules, which affect their intermolecular forces.
Conformational Isomerism

Another way propane can form isomers is through conformational isomerism. Conformational isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and arrangement of atoms but differ in their three-dimensional shape. Propane can form several conformational isomers, including the eclipsed and staggered conformations.
The eclipsed conformation of propane has a higher energy than the staggered conformation, due to the increased repulsion between the eclipsed hydrogen atoms. This energy difference affects the physical properties of propane, such as its viscosity and thermal conductivity.
Stereoisomerism

A third way propane can form isomers is through stereoisomerism. Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and arrangement of atoms but differ in their three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in space. Propane can form stereoisomers, such as the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of 2-propanol, which is a derivative of propane.
The (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of 2-propanol have different optical properties, such as their ability to rotate plane-polarized light. This difference in optical properties is due to the different arrangements of the atoms in space, which affect the way the molecules interact with light.
Practical Applications of Propane Isomers
The different isomers of propane have various practical applications. For example, n-propane is commonly used as a fuel for cooking and heating, while isopropane is used as a solvent and a refrigerant. The conformational isomers of propane are important in understanding its physical properties, such as its viscosity and thermal conductivity. The stereoisomers of propane, such as the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of 2-propanol, are important in understanding their optical properties and their applications in chemistry and biology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, propane can form isomers through structural, conformational, and stereoisomerism. These isomers have different physical and chemical properties, which are important in understanding their practical applications. The study of propane isomers is an important area of research in organic chemistry, as it provides insights into the structure and properties of molecules.
Take Action
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the different ways propane can form isomers. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. We would love to hear from you and provide you with more information on this topic.
What is the difference between structural and conformational isomerism?
+Structural isomerism refers to molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of their atoms. Conformational isomerism refers to molecules that have the same molecular formula and arrangement of atoms but differ in their three-dimensional shape.
What is stereoisomerism?
+Stereoisomerism refers to molecules that have the same molecular formula and arrangement of atoms but differ in their three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in space.
What are the practical applications of propane isomers?
+The different isomers of propane have various practical applications, such as n-propane being used as a fuel for cooking and heating, while isopropane is used as a solvent and a refrigerant.