Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is a diatomic molecule composed of hydrogen and chlorine atoms. It is a strong acid and a major component of gastric acid in the stomach. While HCl is not typically considered a molecule that forms hydrogen bonds in the classical sense, it can interact with other molecules in ways that resemble hydrogen bonding. In this article, we will explore whether HCl can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules naturally.
Understanding Hydrogen Bonding
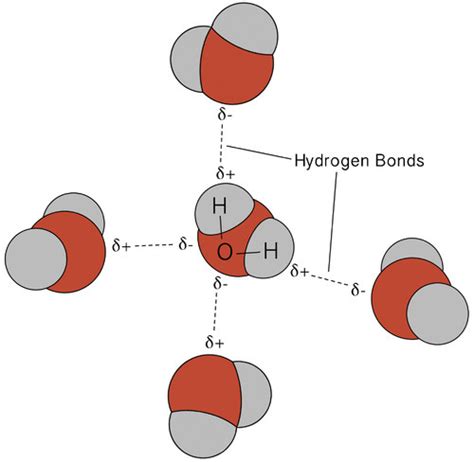
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. This bonding is relatively weak compared to covalent and ionic bonds but plays a crucial role in the structure and properties of many biological molecules, including water, proteins, and DNA.
HCl's Ability to Form Hydrogen Bonds
HCl is a polar molecule, meaning it has a slightly positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a slightly negative charge on the chlorine atom. This polarity allows HCl to interact with other molecules through electrostatic forces. However, the hydrogen atom in HCl is not bonded to an electronegative atom, which is a necessary condition for classical hydrogen bonding.
Despite this, HCl can still interact with other molecules in ways that resemble hydrogen bonding. For example, HCl can form complexes with molecules that have lone pairs of electrons, such as water or ammonia. In these complexes, the hydrogen atom of HCl interacts with the lone pair electrons of the other molecule, forming a weak bond.
Examples of HCl's Interactions with Other Molecules
There are several examples of HCl's interactions with other molecules that resemble hydrogen bonding:
- HCl-Water Complexes: HCl can form complexes with water molecules, where the hydrogen atom of HCl interacts with the oxygen atom of water. These complexes are important in understanding the behavior of HCl in aqueous solutions.
- HCl-Ammonia Complexes: HCl can also form complexes with ammonia molecules, where the hydrogen atom of HCl interacts with the nitrogen atom of ammonia. These complexes are relevant to the study of acid-base chemistry.
- HCl-Protein Interactions: HCl can interact with proteins through hydrogen bonding-like interactions. For example, the hydrogen atom of HCl can interact with the oxygen atom of a carbonyl group in a protein, influencing the protein's structure and function.

Factors Influencing HCl's Ability to Form Hydrogen Bonds
Several factors can influence HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules:
- Concentration: The concentration of HCl can affect its ability to form hydrogen bonds. At high concentrations, HCl molecules may interact with each other, reducing their availability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules.
- Temperature: Temperature can also influence HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds. At higher temperatures, the kinetic energy of the molecules increases, making it more difficult for HCl to form stable hydrogen bonds.
- pH: The pH of the solution can also affect HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds. At low pH values, HCl is more likely to be in its protonated form, which can reduce its ability to form hydrogen bonds.
Conclusion
While HCl is not typically considered a molecule that forms hydrogen bonds in the classical sense, it can interact with other molecules in ways that resemble hydrogen bonding. These interactions are important in understanding the behavior of HCl in various biological and chemical contexts. Factors such as concentration, temperature, and pH can influence HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
Call to Action
Share this article with your friends and colleagues who are interested in chemistry and biology. If you have any questions or topics you would like us to cover in future articles, please let us know in the comments section.
FAQ Section
What is hydrogen bonding?
+Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom.
Can HCl form hydrogen bonds with other molecules?
+While HCl is not typically considered a molecule that forms hydrogen bonds in the classical sense, it can interact with other molecules in ways that resemble hydrogen bonding.
What factors influence HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds?
+Concentration, temperature, and pH can influence HCl's ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules.