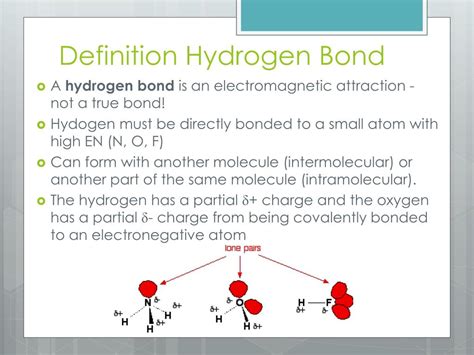
The fascinating world of molecular interactions! Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in shaping the structure and function of molecules, and C-H form hydrogen bonds are no exception. In this article, we'll delve into the three ways C-H form hydrogen bonds, exploring their significance, mechanisms, and examples.
The Importance of Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. These bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds but are essential for the stability and function of biomolecules, such as proteins, DNA, and RNA.
C-H form hydrogen bonds, in particular, involve the interaction between a carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond and an electronegative atom. These bonds are crucial in various biological processes, including protein-ligand interactions, enzyme catalysis, and molecular recognition.

3 Ways C-H Form Hydrogen Bonds
C-H form hydrogen bonds can occur through three distinct mechanisms:
1. C-H...O Hydrogen Bonds
This type of hydrogen bond involves the interaction between a C-H bond and an oxygen atom. The oxygen atom acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor, while the C-H bond serves as a hydrogen bond donor. C-H...O hydrogen bonds are common in biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
For example, in the protein-ligand complex of lysozyme, a C-H...O hydrogen bond forms between the C-H bond of a tryptophan residue and the oxygen atom of a sugar molecule.
2. C-H...N Hydrogen Bonds
In this type of hydrogen bond, the C-H bond interacts with a nitrogen atom. The nitrogen atom acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor, while the C-H bond serves as a hydrogen bond donor. C-H...N hydrogen bonds are often found in protein-nucleic acid interactions and are crucial for the stability of DNA and RNA structures.
For instance, in the DNA double helix, C-H...N hydrogen bonds form between the C-H bonds of adenine and guanine bases and the nitrogen atoms of cytosine and thymine bases.
3. C-H...π Hydrogen Bonds
This type of hydrogen bond involves the interaction between a C-H bond and a π system, such as an aromatic ring or a carbon-carbon double bond. The π system acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor, while the C-H bond serves as a hydrogen bond donor. C-H...π hydrogen bonds are common in protein-ligand interactions and are important for the recognition of aromatic compounds.
For example, in the protein-ligand complex of cytochrome P450, a C-H...π hydrogen bond forms between the C-H bond of a phenylalanine residue and the π system of a heme group.
Mechanisms and Energetics
The mechanisms and energetics of C-H form hydrogen bonds are complex and influenced by various factors, including the electronegativity of the atom involved, the hybridization of the C-H bond, and the environment in which the bond forms.
In general, C-H form hydrogen bonds are weaker than traditional hydrogen bonds, with energies ranging from 1-5 kcal/mol. However, their cumulative effect can significantly contribute to the stability and function of biomolecules.

Examples and Applications
C-H form hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Protein-ligand interactions: C-H form hydrogen bonds are essential for the recognition and binding of ligands to proteins.
- Enzyme catalysis: C-H form hydrogen bonds can participate in the catalytic mechanism of enzymes, facilitating the formation of transition states.
- Molecular recognition: C-H form hydrogen bonds are involved in the recognition of biomolecules, such as DNA and RNA, by proteins and other ligands.
In addition, C-H form hydrogen bonds have applications in drug design and development, where they can be exploited to improve the binding affinity and selectivity of small molecules.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, C-H form hydrogen bonds are a fascinating class of intermolecular forces that play a crucial role in various biological processes. Understanding the mechanisms and energetics of these bonds is essential for the development of new therapeutic strategies and the design of novel biomaterials.
As research continues to uncover the intricacies of C-H form hydrogen bonds, we can expect to see new applications in fields such as drug discovery, biomaterials science, and nanotechnology.

What do you think about C-H form hydrogen bonds? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
What is the difference between C-H form hydrogen bonds and traditional hydrogen bonds?
+C-H form hydrogen bonds involve the interaction between a C-H bond and an electronegative atom, whereas traditional hydrogen bonds involve the interaction between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
What is the significance of C-H form hydrogen bonds in biological processes?
+C-H form hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in various biological processes, including protein-ligand interactions, enzyme catalysis, and molecular recognition.
Can C-H form hydrogen bonds be exploited in drug design and development?
+Yes, C-H form hydrogen bonds can be exploited in drug design and development to improve the binding affinity and selectivity of small molecules.