The atomic structure is one of the fundamental concepts in chemistry, and understanding the electron configuration is essential for explaining the behavior of elements. In this article, we will delve into the world of electron configuration, focusing on the long form of the bromine (Br) electron configuration.
The importance of electron configuration cannot be overstated. It helps us understand the chemical properties of elements, their reactivity, and how they interact with other elements. Electron configuration is also crucial in understanding the periodic table, as it explains the periodic trends and patterns observed in the table.
What is Electron Configuration?
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It describes the distribution of electrons in different energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus. The electron configuration is typically written in a specific notation, which indicates the energy level, orbital type, and number of electrons in each orbital.

Understanding the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are arranged in rows called periods and columns called groups or families.

The Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule
To write the electron configuration of an element, we need to follow two fundamental principles: the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule. The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first, while Hund's rule states that electrons occupy empty orbitals of the same energy level before pairing up in an already occupied orbital.
Aufbau Principle
The Aufbau principle helps us determine the order in which electrons fill the energy levels. The principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels first. This means that the electrons fill the 1s orbital before moving to the 2s orbital, and so on.
Hund's Rule
Hund's rule explains how electrons occupy the orbitals of the same energy level. According to this rule, electrons occupy empty orbitals of the same energy level before pairing up in an already occupied orbital. This means that if there are multiple orbitals of the same energy level, electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up.
5 Steps to Write the Br Electron Configuration in Long Form
Now that we understand the basics of electron configuration and the principles that govern it, let's move on to writing the Br electron configuration in long form. Here are the 5 steps:
Step 1: Determine the Atomic Number
The atomic number of bromine is 35. This means that a neutral bromine atom has 35 electrons.
Step 2: Write the Electron Configuration
Using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, we can write the electron configuration of bromine as follows:
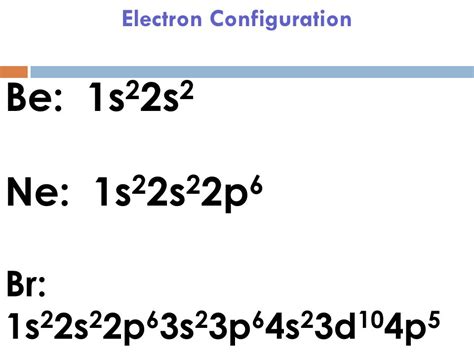
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵

Step 3: Identify the Energy Levels
The electron configuration of bromine can be broken down into different energy levels. The energy levels are:
- 1s² (first energy level)
- 2s² 2p⁶ (second energy level)
- 3s² 3p⁶ (third energy level)
- 4s² 3d¹⁰ (fourth energy level)
- 4p⁵ (fourth energy level)
Step 4: Identify the Orbitals
Each energy level has different orbitals. The orbitals are:
- s-orbitals (spherical shape)
- p-orbitals (dumbbell shape)
- d-orbitals (four-leaf clover shape)
Step 5: Write the Long Form
Using the energy levels and orbitals, we can write the long form of the Br electron configuration as follows:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵
The long form of the electron configuration provides a detailed description of the arrangement of electrons in a bromine atom.

By following these 5 steps, we can write the Br electron configuration in long form. Understanding the electron configuration of elements is essential for explaining their chemical properties and behavior.
If you have any questions or need further clarification on the topic, please don't hesitate to ask in the comments section below. We'd love to hear from you!
What is the atomic number of bromine?
+The atomic number of bromine is 35.
What is the electron configuration of bromine?
+The electron configuration of bromine is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵.
What are the different energy levels in the electron configuration of bromine?
+The different energy levels in the electron configuration of bromine are 1s², 2s² 2p⁶, 3s² 3p⁶, 4s² 3d¹⁰, and 4p⁵.