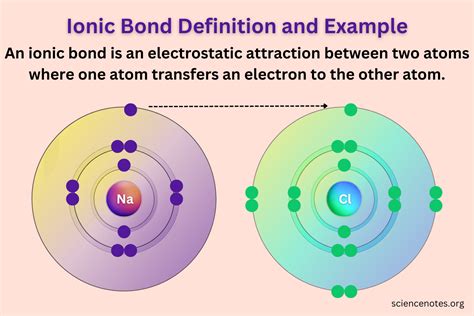
Ionic bonds are a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms that have a large difference in electronegativity. This type of bond is typically found in compounds that consist of metals and nonmetals. In this article, we will explore the two elements that form ionic bonds and understand the process of ionic bond formation.
What are Ionic Bonds?

Ionic bonds are a type of chemical bond that involves the transfer of electrons between two atoms. This type of bond is typically found in compounds that consist of metals and nonmetals. The metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, while the nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the positively charged metal ion and the negatively charged nonmetal ion holds the two ions together and forms an ionic bond.
Elements that Form Ionic Bonds

There are two elements that form ionic bonds:
1. Metals
Metals are a group of elements that are typically found on the left side of the periodic table. These elements have a low electronegativity value, which means that they tend to lose electrons easily. When a metal atom loses one or more electrons, it forms a positively charged ion. This positively charged ion is attracted to a negatively charged ion, which is typically formed by a nonmetal atom.
Examples of metals that form ionic bonds include:
- Sodium (Na)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
2. Nonmetals
Nonmetals are a group of elements that are typically found on the right side of the periodic table. These elements have a high electronegativity value, which means that they tend to gain electrons easily. When a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons, it forms a negatively charged ion. This negatively charged ion is attracted to a positively charged ion, which is typically formed by a metal atom.
Examples of nonmetals that form ionic bonds include:
- Oxygen (O)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Chlorine (Cl)
Process of Ionic Bond Formation

The process of ionic bond formation involves the transfer of electrons between a metal atom and a nonmetal atom. The metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, while the nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the positively charged metal ion and the negatively charged nonmetal ion holds the two ions together and forms an ionic bond.
For example, when sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine (Cl), the sodium atom loses one electron to form a positively charged sodium ion (Na+). The chlorine atom gains one electron to form a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-). The electrostatic attraction between the positively charged sodium ion and the negatively charged chloride ion holds the two ions together and forms an ionic bond.
Characteristics of Ionic Bonds

Ionic bonds have several characteristics that distinguish them from other types of chemical bonds. Some of the key characteristics of ionic bonds include:
- High melting and boiling points: Ionic bonds are typically strong and require a lot of energy to break. As a result, compounds that form ionic bonds tend to have high melting and boiling points.
- Conductivity: Ionic bonds are typically found in compounds that are good conductors of electricity. This is because the ions in an ionic bond are free to move and carry electrical charge.
- Solubility: Ionic bonds are typically found in compounds that are soluble in water. This is because the ions in an ionic bond are attracted to water molecules, which are polar.
Examples of Ionic Bonds

There are many examples of ionic bonds in nature. Some common examples include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl): Sodium chloride, also known as table salt, is a classic example of an ionic bond. The sodium ion (Na+) is attracted to the chloride ion (Cl-), forming a strong ionic bond.
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3): Calcium carbonate is a compound that forms an ionic bond between a calcium ion (Ca2+) and a carbonate ion (CO32-).
- Magnesium oxide (MgO): Magnesium oxide is a compound that forms an ionic bond between a magnesium ion (Mg2+) and an oxygen ion (O2-).
In conclusion, ionic bonds are an important type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms that have a large difference in electronegativity. The two elements that form ionic bonds are metals and nonmetals. The process of ionic bond formation involves the transfer of electrons between a metal atom and a nonmetal atom, resulting in the formation of a positively charged metal ion and a negatively charged nonmetal ion. The electrostatic attraction between the positively charged metal ion and the negatively charged nonmetal ion holds the two ions together and forms an ionic bond.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of ionic bonds and the elements that form them. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them in the section below.
What is an ionic bond?
+An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms that have a large difference in electronegativity. This type of bond is typically found in compounds that consist of metals and nonmetals.
What are the two elements that form ionic bonds?
+The two elements that form ionic bonds are metals and nonmetals. Metals are typically found on the left side of the periodic table, while nonmetals are typically found on the right side of the periodic table.
What is the process of ionic bond formation?
+The process of ionic bond formation involves the transfer of electrons between a metal atom and a nonmetal atom. The metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, while the nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion. The electrostatic attraction between the positively charged metal ion and the negatively charged nonmetal ion holds the two ions together and forms an ionic bond.