The world of chemistry is fascinating, and one of the most fundamental concepts is the way atoms combine to form compounds and molecules. This process is the building block of everything around us, from the air we breathe to the stars in the sky. In this article, we'll delve into the world of atomic combinations, exploring the ways in which atoms come together to form new substances.
What are Atoms?

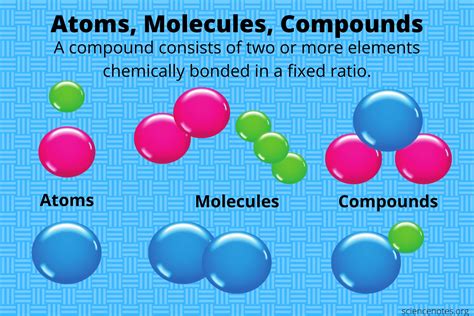
Atoms are the smallest units of matter that still retain the properties of an element. They consist of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, or center, of the atom, while electrons orbit around the outside. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
What are Compounds and Molecules?

Compounds and molecules are formed when atoms combine with each other. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together. A compound is a substance that is formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together. Compounds can be composed of molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
How Do Atoms Combine?
Atoms combine through chemical bonds, which are forces that hold atoms together. There are several types of chemical bonds, including covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds.
- Covalent bonds are formed when two or more atoms share electrons.
- Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
- Metallic bonds are formed when electrons are delocalized, or spread out, among a lattice of atoms.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are the most common type of chemical bond. They are formed when two or more atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level. This sharing of electrons leads to a strong attraction between the atoms, holding them together.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This transfer of electrons leads to the formation of ions, which are atoms that have gained or lost electrons. The electrostatic attraction between the ions holds them together, forming a compound.
Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds are formed when electrons are delocalized, or spread out, among a lattice of atoms. This delocalization of electrons leads to a strong attraction between the atoms, holding them together.
Examples of Atomic Combinations

There are many examples of atomic combinations in everyday life. Some examples include:
- Water (H2O) - a compound formed from the combination of hydrogen and oxygen atoms
- Salt (NaCl) - a compound formed from the combination of sodium and chlorine atoms
- Sugar (C6H12O6) - a compound formed from the combination of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
Importance of Atomic Combinations
Atomic combinations are essential for life as we know it. They are the building blocks of everything around us, from the air we breathe to the stars in the sky. Without atomic combinations, life would not be possible.
Conclusion
Atomic combinations are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and they play a crucial role in the formation of compounds and molecules. By understanding how atoms combine, we can better understand the world around us and the processes that shape it. Whether you're a student of chemistry or simply interested in the natural world, the study of atomic combinations is a fascinating and rewarding field of study.
What is the smallest unit of matter?
+The smallest unit of matter is the atom.
What is the difference between a compound and a molecule?
+A compound is a substance that is formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together, while a molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together.
What type of bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms?
+A covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms.