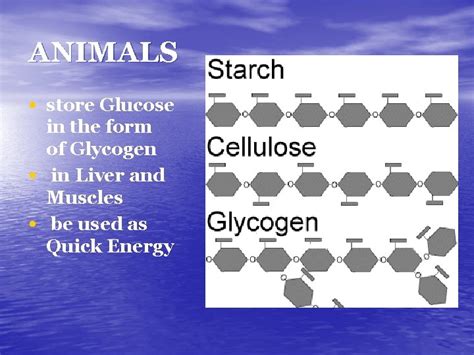
The human body is incredibly efficient at storing energy for future use. One of the primary ways it accomplishes this is through the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. But did you know that animals also store glucose in the form of glycogen? In this article, we will delve into the world of animal physiology and explore how animals store glucose, the benefits of glycogen storage, and the different types of glycogen found in various animal species.
What is Glycogen?

Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate, also known as animal starch, that serves as a primary energy storage molecule in animals. It is composed of long chains of glucose molecules linked together through glycosidic bonds. Glycogen is synthesized from glucose molecules through a process called glycogenesis, which involves the action of several enzymes. The resulting glycogen molecule is highly branched, allowing for rapid breakdown and release of glucose when energy is needed.
How Do Animals Store Glycogen?
Animals store glycogen in various tissues, including the liver, muscles, and kidneys. The liver is the primary site of glycogen storage, with approximately 100-150 grams of glycogen stored in the liver of a healthy adult human. Muscle tissue also stores glycogen, with the amount varying depending on factors such as muscle type, fiber size, and exercise level.
In animals, glycogen is stored in the form of granules or rosettes, which are composed of glycogen molecules surrounded by a protein coat. These granules are found in the cytoplasm of cells and can be quickly broken down to release glucose when energy is needed.
Benefits of Glycogen Storage in Animals

Glycogen storage provides several benefits to animals, including:
- Rapid energy release: Glycogen can be quickly broken down to release glucose, providing a rapid source of energy for animals.
- Energy storage: Glycogen serves as an energy reservoir, allowing animals to store energy for future use.
- Muscle function: Glycogen is an important energy source for muscle contraction and relaxation.
- Hormone regulation: Glycogen storage is regulated by hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which play a critical role in maintaining blood glucose levels.
Types of Glycogen in Animals
There are several types of glycogen found in animals, including:
- Liver glycogen: Stored in the liver, this type of glycogen is broken down to release glucose into the bloodstream.
- Muscle glycogen: Stored in muscle tissue, this type of glycogen is broken down to provide energy for muscle contraction.
- Kidney glycogen: Stored in the kidneys, this type of glycogen is broken down to provide energy for kidney function.
Comparison of Glycogen Storage in Different Animal Species

Glycogen storage varies across different animal species, with some species storing more glycogen than others. For example:
- Humans: Store approximately 100-150 grams of glycogen in the liver.
- Rats: Store approximately 200-300 grams of glycogen in the liver.
- Fish: Store glycogen in the form of granules in the liver and muscle tissue.
- Insects: Store glycogen in the form of trehalose, a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules.
Factors Affecting Glycogen Storage in Animals
Several factors can affect glycogen storage in animals, including:
- Diet: A diet high in carbohydrates can increase glycogen storage, while a diet low in carbohydrates can decrease glycogen storage.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can increase glycogen storage in muscle tissue.
- Hormones: Hormones such as insulin and glucagon play a critical role in regulating glycogen storage.
Conclusion
Animals store glucose in the form of glycogen, which provides a rapid source of energy and serves as an energy reservoir. Glycogen storage varies across different animal species, with some species storing more glycogen than others. Understanding glycogen storage in animals can provide insights into the physiology of energy metabolism and the importance of glucose storage in maintaining proper bodily function.
We hope you found this article informative and engaging! If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is glycogen?
+Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that serves as a primary energy storage molecule in animals.
Where is glycogen stored in animals?
+Glycogen is stored in the liver, muscles, and kidneys of animals.
What are the benefits of glycogen storage in animals?
+Glycogen storage provides several benefits, including rapid energy release, energy storage, muscle function, and hormone regulation.