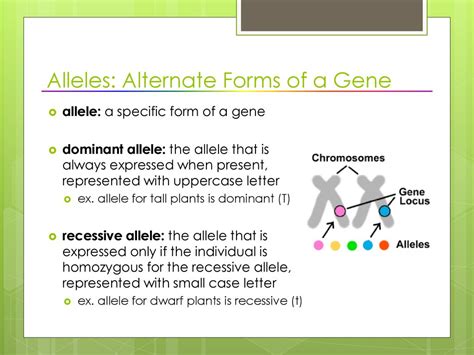
The concept of alleles is a fundamental aspect of genetics, and understanding what an allele is can help us grasp the intricacies of genetic variation and inheritance.
Genetics is the study of heredity, genes, and variation. It's a field that has revolutionized our understanding of life and has numerous applications in fields like medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. At the heart of genetics is the concept of genes, which are the basic units of heredity. However, genes are not static entities; they can exist in different forms, known as alleles.

What Is An Allele?
An allele is an alternative form of a gene that occupies a specific location on a chromosome. In other words, alleles are different versions of the same gene. These different versions can result in different traits or characteristics, such as eye color, hair color, or height.
To understand alleles better, let's consider a simple example. Suppose we're looking at the gene that determines eye color. In this case, there are two possible alleles: one for blue eyes (B) and one for brown eyes (b). These alleles are different forms of the same gene and occupy the same location on the chromosome.
Types Of Alleles
Alleles can be categorized into different types based on their function and the effect they have on the trait they influence.
- Dominant Allele: A dominant allele is one that will always be expressed if an individual has one copy of the allele. For example, the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant, while the allele for blue eyes (b) is recessive. If an individual has one copy of the B allele and one copy of the b allele (Bb), they will have brown eyes because the dominant allele (B) masks the effect of the recessive allele (b).
- Recessive Allele: A recessive allele is one that will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the allele. In our eye color example, the allele for blue eyes (b) is recessive. An individual needs to have two copies of the b allele (bb) to express blue eyes.
- Codominant Alleles: Codominant alleles are two different alleles that have an equal effect on the trait. Neither allele is dominant or recessive, and the individual will express a combination of the two traits. For example, in the ABO blood group system, the A and B alleles are codominant. An individual with the genotype AB will express both A and B antigens on their red blood cells.

How Do Alleles Influence Traits?
Alleles play a crucial role in determining the traits of an individual. The combination of alleles an individual inherits from their parents determines the expression of a particular trait. Let's consider the following scenarios:
- Homozygous: An individual has two copies of the same allele (BB or bb). In this case, the individual will express the trait associated with that allele.
- Heterozygous: An individual has one copy of each allele (Bb). In this case, the dominant allele (B) will mask the effect of the recessive allele (b), and the individual will express the trait associated with the dominant allele.
- Genotype And Phenotype: The genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while the phenotype refers to the physical expression of the trait. The combination of alleles an individual inherits determines their genotype, which in turn determines their phenotype.
Allele Frequency And Population Genetics
Allele frequency refers to the proportion of a particular allele in a population. Population genetics is the study of the distribution of alleles in a population over time. Understanding allele frequency and population genetics is essential in fields like medicine, where it can help us identify genetic risk factors for diseases.

Practical Applications Of Alleles
The concept of alleles has numerous practical applications in fields like medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual's genotype to identify genetic disorders or diseases. Understanding alleles is essential in genetic testing, as it helps us identify the genetic risk factors associated with a particular disease.
- Genetic Engineering: Genetic engineering involves manipulating an organism's genes to introduce desirable traits. Understanding alleles is crucial in genetic engineering, as it helps us identify the specific genes and alleles associated with a particular trait.
- Agriculture: In agriculture, understanding alleles can help us develop crops that are resistant to diseases or pests. By identifying the specific alleles associated with these traits, we can breed crops that are more resilient and productive.

Conclusion
In conclusion, alleles are alternative forms of a gene that play a crucial role in determining the traits of an individual. Understanding alleles is essential in fields like medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology, where it can help us identify genetic risk factors, develop new treatments, and breed crops that are more resilient and productive.
By grasping the concept of alleles, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intricacies of genetic variation and inheritance. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or simply someone interested in genetics, understanding alleles is a fundamental aspect of understanding the building blocks of life.

We hope this article has helped you understand the concept of alleles and their significance in genetics. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is an allele?
+An allele is an alternative form of a gene that occupies a specific location on a chromosome.
What are the different types of alleles?
+There are three types of alleles: dominant, recessive, and codominant.
How do alleles influence traits?
+Alleles play a crucial role in determining the traits of an individual. The combination of alleles an individual inherits from their parents determines the expression of a particular trait.