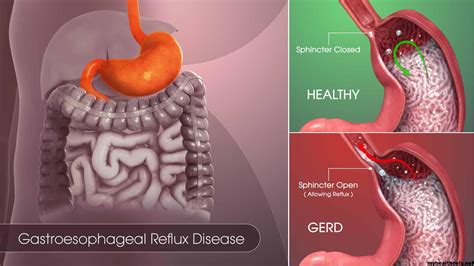
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, commonly referred to as GERD, is a chronic condition in which the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort, pain, and potentially leading to complications. This condition is often referred to as acid reflux or heartburn, but it's essential to understand that GERD is a more severe and persistent problem that requires medical attention.
GERD affects millions of people worldwide, and its prevalence is increasing due to various factors, including obesity, diet, and lifestyle. Despite its commonality, many individuals are not aware of the severity of GERD and its potential consequences. In this article, we will delve into the world of gastroesophageal reflux disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition.
Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease

GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to function properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. The LES is a ring-like muscle that separates the esophagus and stomach, and its primary function is to keep the stomach acid from entering the esophagus. When the LES relaxes or becomes weak, stomach acid can flow back into the esophagus, causing inflammation, irritation, and damage to the esophageal lining.
Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Several factors contribute to the development of GERD, including:
- Obesity: Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, causing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- Diet: Consuming certain foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, spicy foods, and caffeine, can trigger GERD symptoms.
- Lifestyle: Smoking, lack of physical activity, and eating large meals can exacerbate GERD.
- Hiatal hernia: A condition in which the stomach bulges up into the chest through an opening in the diaphragm.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause the LES to relax, leading to GERD symptoms.
Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease

The symptoms of GERD can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often accompanied by a sour or bitter taste in the mouth.
- Regurgitation: Food or sour liquid flowing back into the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing: Trouble swallowing food or feeling like food is stuck in the throat.
- Chest pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest, often radiating to the arm, neck, or jaw.
- Coughing: Chronic coughing or wheezing due to acid reflux.
Diagnosing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Diagnosing GERD typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Endoscopy: A procedure in which a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to visualize the esophagus and stomach.
- Ambulatory acid probe tests: A test that measures the acidity of the esophagus over a 24-hour period.
- Upper GI series: A test that uses X-rays to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine.
Treatment Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease

Treatment for GERD typically involves lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery. Lifestyle changes include:
- Weight loss
- Avoiding trigger foods and drinks
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Raising the head of the bed
- Quitting smoking
Medications for GERD include:
- Antacids: Over-the-counter medications that neutralize stomach acid.
- Histamine-2 (H2) blockers: Medications that reduce acid production in the stomach.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): Medications that block the production of stomach acid.
Surgery may be necessary for severe cases of GERD, including:
- Fundoplication: A procedure in which the upper portion of the stomach is wrapped around the lower portion of the esophagus.
- LINX Reflux Management System: A minimally invasive procedure that involves placing a ring of magnetic beads around the LES.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
In addition to medical treatment, making lifestyle changes can help manage GERD symptoms. Some tips include:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoiding trigger foods and drinks.
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing.
- Getting regular exercise.
- Quitting smoking.
Complications of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease

If left untreated, GERD can lead to complications, including:
- Esophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus.
- Stricture: Narrowing of the esophagus due to chronic inflammation.
- Barrett's esophagus: A precancerous condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes.
- Respiratory problems: Asthma, chronic coughing, and pneumonia.
Living with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Living with GERD requires making lifestyle changes and managing symptoms. Some tips for living with GERD include:
- Keeping a food diary to track trigger foods and drinks.
- Avoiding eating before bedtime.
- Raising the head of the bed.
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques.
- Getting regular exercise.
What is gastroesophageal reflux disease?
+Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition in which the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort, pain, and potentially leading to complications.
What are the symptoms of GERD?
+The symptoms of GERD include heartburn, regurgitation, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and coughing.
How is GERD diagnosed?
+GERD is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including endoscopy, ambulatory acid probe tests, and upper GI series.