As the population ages, an increasing number of individuals are reaching retirement age and beginning to withdraw from their retirement accounts. One of the most common forms used to report these distributions is the 1040 R form. In this article, we will delve into the world of retirement distributions, explaining the ins and outs of the 1040 R form and providing guidance on how to navigate this complex process.
The Importance of Accurate Reporting
Accurate reporting of retirement distributions is crucial for ensuring compliance with tax laws and avoiding any potential penalties. The 1040 R form is used to report distributions from various types of retirement accounts, including 401(k), IRA, and pension plans. These distributions are considered taxable income and must be reported on an individual's tax return.
Understanding the 1040 R Form
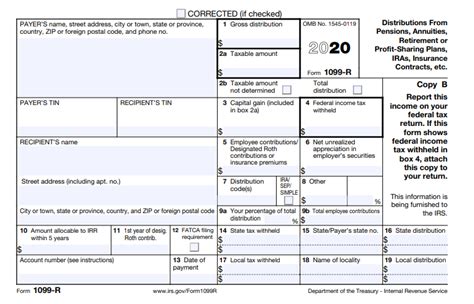
The 1040 R form is used to report distributions from retirement accounts that are subject to income tax withholding. The form is typically filed by the payer of the distribution, such as the plan administrator or financial institution. The form reports the gross distribution amount, federal income tax withheld, and any state or local taxes withheld.

Key Components of the 1040 R Form
The 1040 R form is composed of several key components, including:
- Payer's Name and Address: The name and address of the payer, such as the plan administrator or financial institution.
- Recipient's Name and Address: The name and address of the recipient, such as the individual receiving the distribution.
- Account Number: The account number associated with the retirement account.
- Gross Distribution: The total amount of the distribution, before any taxes are withheld.
- Federal Income Tax Withheld: The amount of federal income tax withheld from the distribution.
- State or Local Taxes Withheld: The amount of state or local taxes withheld from the distribution.
Types of Retirement Distributions
There are several types of retirement distributions that can be reported on the 1040 R form, including:
- Periodic Payments: Regular payments made from a retirement account, such as a pension or annuity.
- Non-Periodic Payments: One-time payments made from a retirement account, such as a lump-sum distribution.
- Rollover Distributions: Distributions that are rolled over into another retirement account, such as an IRA.
Tax Implications of Retirement Distributions
Retirement distributions are considered taxable income and must be reported on an individual's tax return. The tax implications of retirement distributions depend on the type of distribution and the individual's tax situation.
- Ordinary Income: Most retirement distributions are taxed as ordinary income, which means they are subject to income tax.
- Capital Gains: Some retirement distributions, such as those from a Roth IRA, may be taxed as capital gains.
- Withholding: Federal income tax withholding is typically required on retirement distributions, unless the individual elects to opt out.
Penalties for Failure to Comply
Failure to accurately report retirement distributions on the 1040 R form can result in penalties and fines. Some common penalties include:
- Late Filing Penalty: A penalty for failing to file the 1040 R form on time.
- Accuracy-Related Penalty: A penalty for failing to accurately report retirement distributions.
- Failure to Withhold Penalty: A penalty for failing to withhold federal income tax from retirement distributions.
Best Practices for Accurate Reporting
To ensure accurate reporting of retirement distributions, individuals should:
- Verify Information: Verify the accuracy of information reported on the 1040 R form.
- Keep Records: Keep accurate records of retirement distributions, including the date, amount, and type of distribution.
- Consult a Tax Professional: Consult a tax professional to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When reporting retirement distributions on the 1040 R form, individuals should avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Failing to Report Distributions: Failing to report retirement distributions on the 1040 R form.
- Inaccurate Reporting: Inaccurately reporting retirement distributions, such as reporting the wrong amount or type of distribution.
- Failure to Withhold: Failing to withhold federal income tax from retirement distributions.

Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the 1040 R form is an important document used to report retirement distributions. Accurate reporting of these distributions is crucial for ensuring compliance with tax laws and avoiding potential penalties. By understanding the key components of the 1040 R form and following best practices for accurate reporting, individuals can ensure a smooth and stress-free tax filing experience.
If you have any questions or concerns about reporting retirement distributions on the 1040 R form, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful. Additionally, we invite you to explore our other resources on retirement planning and tax compliance.
What is the 1040 R form used for?
+The 1040 R form is used to report distributions from retirement accounts, such as 401(k), IRA, and pension plans.
What are the key components of the 1040 R form?
+The key components of the 1040 R form include the payer's name and address, recipient's name and address, account number, gross distribution, federal income tax withheld, and state or local taxes withheld.
What are the tax implications of retirement distributions?
+Retirement distributions are considered taxable income and must be reported on an individual's tax return. The tax implications depend on the type of distribution and the individual's tax situation.