Underwater mountains, also known as mid-ocean ridges, are vast mountain ranges that run through the middle of the oceans. These mountain ranges are formed by the movement of tectonic plates, which are large sections of the Earth's crust that fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. As these plates move apart, magma from the Earth's mantle rises to fill the gap, creating new oceanic crust. This process is known as seafloor spreading. Convection currents play a crucial role in the formation of underwater mountains, and there are three main ways in which they form.
What are Convection Currents?

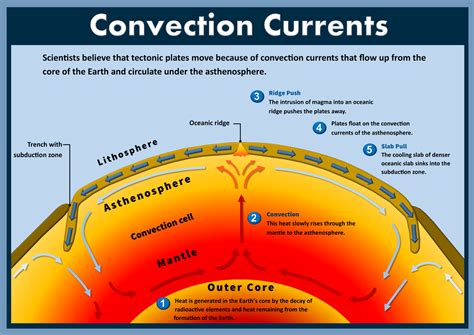
Convection currents are the movement of fluids caused by heat transfer. In the context of underwater mountains, convection currents refer to the movement of magma and fluids in the Earth's mantle. As the mantle rocks heat up, they expand and become less dense than the surrounding rocks. This causes them to rise, creating a circulation of fluid known as a convection current.
How Convection Currents Form Underwater Mountains
Convection currents play a crucial role in the formation of underwater mountains. Here are three ways in which they form:
1. Plate Tectonics and Seafloor Spreading

The movement of tectonic plates is the primary driver of convection currents in the formation of underwater mountains. As the plates move apart, the mantle rocks beneath them heat up, causing them to rise and create a convection current. This current carries magma and fluids from the mantle to the surface, where they solidify and form new oceanic crust.
Process of Seafloor Spreading
The process of seafloor spreading involves the creation of new oceanic crust as magma rises from the mantle and solidifies at the surface. This process occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where the tectonic plates are moving apart. As the magma rises, it cools and solidifies, forming new crust that is pushed away from the ridge by the convection current.
2. Mantle Plumes and Hotspots

Mantle plumes are upwellings of hot rock that rise from the Earth's core-mantle boundary to the surface. These plumes can create convection currents in the mantle, which can contribute to the formation of underwater mountains. Hotspots are areas where mantle plumes reach the surface, creating volcanic activity and the formation of seamounts and oceanic islands.
Formation of Seamounts and Oceanic Islands
Seamounts and oceanic islands are formed when mantle plumes reach the surface, creating volcanic activity and the eruption of magma. This magma solidifies and forms new crust, which can build up over time to form seamounts and oceanic islands. Convection currents play a crucial role in the formation of these features, carrying magma and fluids from the mantle to the surface.
3. Edge-Driven Convection

Edge-driven convection occurs when the edges of tectonic plates interact with the mantle, creating convection currents that drive the formation of underwater mountains. This process occurs at subduction zones, where one plate is being pushed beneath another.
Formation of Trenches and Volcanic Arcs
Edge-driven convection can create trenches and volcanic arcs, which are characteristic features of subduction zones. As the plate is pushed beneath the mantle, it encounters increasing heat and pressure, causing the rocks to melt and form magma. This magma rises to the surface, creating volcanic activity and the formation of volcanic arcs.
In conclusion, convection currents play a crucial role in the formation of underwater mountains. The three main ways in which they form are through plate tectonics and seafloor spreading, mantle plumes and hotspots, and edge-driven convection. Understanding these processes is essential for grasping the complex geology of underwater mountains and the role they play in shaping our planet.
We hope you found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and family who might be interested in learning more about underwater mountains and convection currents.
What are convection currents?
+Convection currents are the movement of fluids caused by heat transfer. In the context of underwater mountains, convection currents refer to the movement of magma and fluids in the Earth's mantle.
What is seafloor spreading?
+Seafloor spreading is the process by which new oceanic crust is created as magma rises from the mantle and solidifies at the surface.
What is a mantle plume?
+A mantle plume is an upwelling of hot rock that rises from the Earth's core-mantle boundary to the surface.