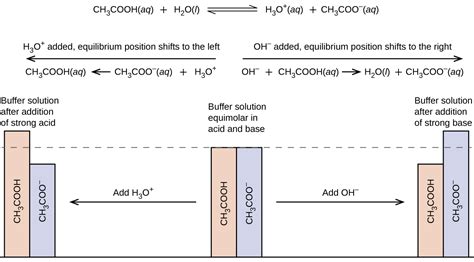
The pH of a solution is a critical parameter in many chemical and biological processes. A buffer solution is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid, that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. One common buffer system is a mixture of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl). This article will explore five ways HCl and NaCl can form a buffer.
The Importance of Buffers in Chemistry and Biology
Buffers play a crucial role in maintaining the pH of a solution, which is essential in many chemical and biological processes. In biological systems, buffers help maintain the pH of bodily fluids, such as blood, which is necessary for proper enzyme function and cell metabolism. In chemical systems, buffers are used to control the pH of solutions, which is critical in many industrial processes, such as the production of pharmaceuticals and food products.

What is a Buffer Solution?
A buffer solution is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The weak acid and its conjugate base, or the weak base and its conjugate acid, work together to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. This is known as the buffering capacity of the solution.
How HCl and NaCl Form a Buffer
HCl is a strong acid that completely dissociates in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+) and chloride ions (Cl-). NaCl is a salt that dissociates in water to produce sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-). When HCl and NaCl are mixed together, they form a buffer solution. Here are five ways HCl and NaCl can form a buffer:
1. Acid-Base Reaction
When HCl is added to a solution containing NaCl, the hydrogen ions (H+) from the HCl react with the chloride ions (Cl-) from the NaCl to form hydrochloric acid (HCl). This reaction reduces the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, which in turn reduces the acidity of the solution.
HCl (aq) + Cl- (aq) ⇌ HCl (aq)
This reaction is an example of an acid-base reaction, where the acid (HCl) reacts with the base (Cl-) to form a salt (HCl) and water.

2. Conjugate Acid-Base Reaction
When NaCl is added to a solution containing HCl, the chloride ions (Cl-) from the NaCl react with the hydrogen ions (H+) from the HCl to form hydrochloric acid (HCl). This reaction reduces the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, which in turn reduces the acidity of the solution.
Cl- (aq) + H+ (aq) ⇌ HCl (aq)
This reaction is an example of a conjugate acid-base reaction, where the conjugate base (Cl-) reacts with the conjugate acid (H+) to form a salt (HCl) and water.

3. Common Ion Effect
When HCl and NaCl are mixed together, they form a common ion, chloride (Cl-). The common ion effect is a phenomenon where the presence of a common ion reduces the solubility of a salt. In this case, the presence of chloride ions (Cl-) from the NaCl reduces the solubility of the HCl, which in turn reduces the acidity of the solution.
4. pH Buffering
When HCl and NaCl are mixed together, they form a buffer solution that resists changes in pH. The pH of the solution is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The buffer solution resists changes in pH by adjusting the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
5. Equilibrium Reaction
When HCl and NaCl are mixed together, they form an equilibrium reaction. The equilibrium reaction is a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. The equilibrium reaction is:
HCl (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
This reaction is an example of an equilibrium reaction, where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.

Conclusion
In conclusion, HCl and NaCl can form a buffer solution through various mechanisms, including acid-base reaction, conjugate acid-base reaction, common ion effect, pH buffering, and equilibrium reaction. The buffer solution resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. This is essential in many chemical and biological processes, where maintaining a stable pH is critical.
Call to Action
If you have any questions or comments about this article, please leave a comment below. Share this article with your friends and colleagues who may be interested in learning more about buffers. If you would like to learn more about buffers and their applications, please visit our website for more information.
What is a buffer solution?
+A buffer solution is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid, that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
What are the five ways HCl and NaCl can form a buffer?
+The five ways HCl and NaCl can form a buffer are: acid-base reaction, conjugate acid-base reaction, common ion effect, pH buffering, and equilibrium reaction.
Why is pH buffering important in biological systems?
+pH buffering is important in biological systems because it helps maintain the pH of bodily fluids, which is necessary for proper enzyme function and cell metabolism.