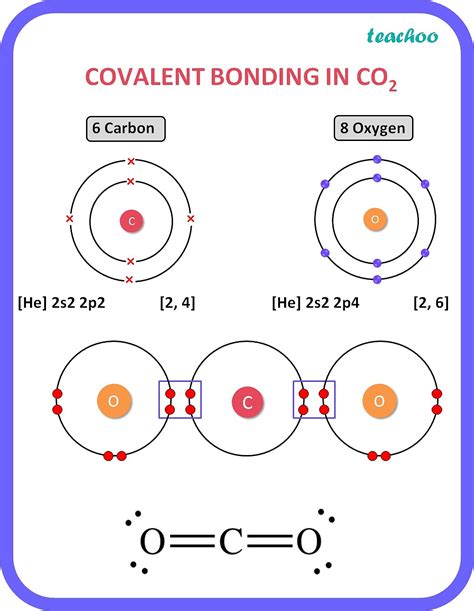
Carbon is the foundation of life on Earth, and its unique ability to form covalent bonds is the reason why it's the basis of all living organisms. From the simplest bacteria to complex human beings, carbon's covalent bonds play a crucial role in forming the molecules that make up our bodies. But what makes carbon so special? In this article, we'll explore the five reasons why carbon forms covalent bonds and why this property is essential for life.
Carbon's Unique Electron Configuration
Carbon's electron configuration is the key to its ability to form covalent bonds. With six electrons in its outermost energy level, carbon has four valence electrons that are available for bonding. This unique configuration allows carbon to form four covalent bonds with other atoms, which is a crucial property for forming complex molecules.

Carbon's Ability to Form Multiple Bonds
Another reason carbon forms covalent bonds is its ability to form multiple bonds with other atoms. Carbon can form single, double, and even triple bonds with other atoms, which allows it to form a wide variety of molecules. This property is essential for forming complex molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and DNA.
Carbon's Electronegativity
Carbon's electronegativity is another factor that contributes to its ability to form covalent bonds. With an electronegativity value of 2.5, carbon is able to attract electrons towards itself, which allows it to form strong covalent bonds with other atoms. This property is essential for forming stable molecules that can withstand the challenges of the environment.

Carbon's Ability to Form Ring Structures
Carbon's ability to form ring structures is another reason why it forms covalent bonds. Carbon can form rings with other carbon atoms, which allows it to form complex molecules like sugars and steroids. This property is essential for forming molecules that have specific shapes and functions.
Carbon's Versatility
Finally, carbon's versatility is another reason why it forms covalent bonds. Carbon can form bonds with a wide variety of atoms, including hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. This property allows carbon to form a wide variety of molecules that have different shapes, functions, and properties.

Types of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are classified into several types, including:
- Sigma (σ) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals along the bond axis.
- Pi (π) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals perpendicular to the bond axis.
- Delta (δ) bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals in a delta-shaped configuration.

Importance of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are essential for forming the molecules that make up our bodies. They provide the structure and function that allows us to move, think, and live. Without covalent bonds, life as we know it would not be possible.
Applications of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Covalent bonds are used to form medicines that can target specific diseases and conditions.
- Materials Science: Covalent bonds are used to form materials with specific properties, such as strength, conductivity, and optical properties.
- Energy: Covalent bonds are used to form fuels that can power our homes, cars, and industries.

Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon's ability to form covalent bonds is the reason why it's the foundation of life on Earth. Its unique electron configuration, ability to form multiple bonds, electronegativity, ability to form ring structures, and versatility make it an ideal element for forming complex molecules. Understanding covalent bonds is essential for understanding the chemistry of life and the world around us.
Call to Action
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of covalent bonds and their importance in forming the molecules that make up our bodies. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the importance of covalent bonds.
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a chemical bond that forms between two atoms when they share one or more pairs of electrons.
Why is carbon able to form covalent bonds?
+Carbon is able to form covalent bonds due to its unique electron configuration, ability to form multiple bonds, electronegativity, ability to form ring structures, and versatility.
What are the types of covalent bonds?
+Covalent bonds are classified into several types, including sigma (σ) bonds, pi (π) bonds, and delta (δ) bonds.