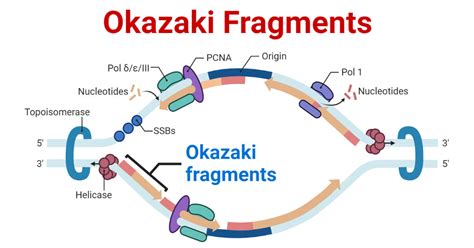
DNA replication is a crucial process that ensures the duplication of genetic material during cell division. However, this complex process is not without its challenges. One of the obstacles that arises during DNA replication is the formation of Okazaki fragments. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNA replication and explore the five reasons why Okazaki fragments form during this process.

The Basics of DNA Replication
Before we dive into the reasons why Okazaki fragments form, let's take a brief look at the process of DNA replication. DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is semi-conservative, meaning that the new DNA molecule is composed of one old strand (the template) and one newly synthesized strand.
The Role of DNA Polymerase
DNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands during replication. However, DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in one direction, from 5' to 3'. This means that on the lagging strand, DNA synthesis occurs in short, discontinuous segments called Okazaki fragments.
5 Reasons Okazaki Fragments Form During DNA Replication
1. DNA Polymerase's 5' to 3' Directionality
As mentioned earlier, DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in one direction, from 5' to 3'. This means that on the lagging strand, DNA synthesis occurs in short segments, resulting in the formation of Okazaki fragments.
2. The Lagging Strand's Antiparallel Structure
The lagging strand is antiparallel to the leading strand, meaning that it runs in the opposite direction. This antiparallel structure makes it difficult for DNA polymerase to synthesize DNA continuously, resulting in the formation of Okazaki fragments.
3. The Need for RNA Primers
RNA primers are short RNA molecules that provide a starting point for DNA synthesis. On the lagging strand, RNA primers are necessary to initiate DNA synthesis, but they are not integrated into the final DNA molecule. As a result, the DNA synthesized from each RNA primer forms a separate Okazaki fragment.
4. The Limitations of DNA Polymerase's Processivity
DNA polymerase's processivity refers to its ability to synthesize DNA continuously without dissociating from the template. However, DNA polymerase's processivity is limited, and it can only synthesize DNA for a certain distance before dissociating. This limited processivity results in the formation of Okazaki fragments.
5. The Presence of Nicking Enzymes
Nicking enzymes, such as endonucleases, can cleave the phosphodiester backbone of DNA, creating nicks. These nicks can serve as starting points for DNA synthesis, resulting in the formation of Okazaki fragments.

The Importance of Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki fragments play a crucial role in DNA replication. They allow DNA polymerase to synthesize DNA on the lagging strand, despite its 5' to 3' directionality. Okazaki fragments are also important for maintaining genome stability, as they provide a mechanism for repairing DNA damage.
Repairing Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki fragments are repaired through a process called DNA ligation. DNA ligase seals the gaps between Okazaki fragments, forming a continuous DNA strand.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Okazaki fragments form during DNA replication due to the limitations of DNA polymerase's directionality, the lagging strand's antiparallel structure, the need for RNA primers, the limitations of DNA polymerase's processivity, and the presence of nicking enzymes. Understanding the reasons why Okazaki fragments form is essential for appreciating the complexities of DNA replication and the importance of maintaining genome stability.
We'd love to hear from you!
Do you have any questions about Okazaki fragments or DNA replication? Share your thoughts in the comments below, and let's start a discussion!
What are Okazaki fragments?
+Okazaki fragments are short, discontinuous segments of DNA that form on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
Why do Okazaki fragments form?
+Okazaki fragments form due to the limitations of DNA polymerase's directionality, the lagging strand's antiparallel structure, the need for RNA primers, the limitations of DNA polymerase's processivity, and the presence of nicking enzymes.
What is the importance of Okazaki fragments?
+Okazaki fragments play a crucial role in DNA replication, allowing DNA polymerase to synthesize DNA on the lagging strand and maintaining genome stability.