The world of carbohydrates is fascinating, with its complex structures and vital functions in our bodies. One of the most interesting aspects of carbohydrates is the formation of disaccharides, which are sugars composed of two molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of disaccharides and explore the two molecules that form them.
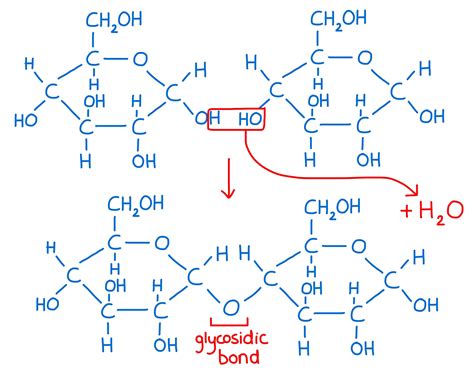
Disaccharides are a type of carbohydrate that consists of two monosaccharide molecules linked together through a glycosidic bond. This bond is formed when two monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, are joined together, resulting in a disaccharide. The two molecules that form a disaccharide are:
Monosaccharides: The Building Blocks of Disaccharides

Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be broken down into simpler sugars. They are the basic building blocks of carbohydrates and are classified into two main categories: aldoses and ketoses. Aldoses have an aldehyde group at one end of the molecule, while ketoses have a ketone group.
Glucose: A Common Monosaccharide
Glucose is a common monosaccharide that is widely found in nature. It is a hexose, meaning it has six carbon atoms, and is a primary source of energy for many living organisms. Glucose is also a component of many disaccharides, including sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Fructose: A Simple Sugar
Fructose is another common monosaccharide that is found in many fruits and vegetables. It is also a hexose and is a component of sucrose, a disaccharide found in table sugar. Fructose is also used as a sweetener in many food products.
The Formation of Disaccharides

Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharide molecules are linked together through a glycosidic bond. This bond is formed when the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide reacts with the anomeric carbon of another monosaccharide. The resulting disaccharide has a unique structure and properties that are different from those of the individual monosaccharides.
Sucrose: A Common Disaccharide
Sucrose is a common disaccharide that is found in table sugar. It is composed of glucose and fructose molecules linked together through a glycosidic bond. Sucrose is widely used as a sweetener in many food products and is an important source of energy for many living organisms.
Types of Disaccharides

There are several types of disaccharides, including:
- Sucrose (glucose + fructose)
- Lactose (glucose + galactose)
- Maltose (glucose + glucose)
- Trehalose (glucose + glucose)
Each type of disaccharide has a unique structure and properties that are different from those of the individual monosaccharides.
Importance of Disaccharides

Disaccharides play a vital role in many biological processes, including energy production and storage. They are also an important component of many food products and are used as sweeteners and texture modifiers.
Energy Production
Disaccharides are an important source of energy for many living organisms. They are broken down into monosaccharides, which are then used to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Food Products
Disaccharides are widely used in many food products, including baked goods, candies, and sweetened beverages. They are used as sweeteners and texture modifiers, adding flavor and texture to many foods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, disaccharides are an important class of carbohydrates that are composed of two monosaccharide molecules linked together through a glycosidic bond. The two molecules that form a disaccharide are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose. Disaccharides play a vital role in many biological processes, including energy production and storage, and are an important component of many food products.
What is a disaccharide?
+A disaccharide is a type of carbohydrate that consists of two monosaccharide molecules linked together through a glycosidic bond.
What are the two molecules that form a disaccharide?
+The two molecules that form a disaccharide are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose.
What is the importance of disaccharides?
+Disaccharides play a vital role in many biological processes, including energy production and storage, and are an important component of many food products.