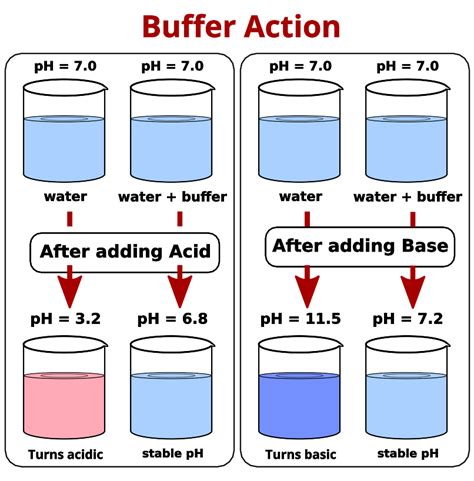
Understanding Buffer Solutions and Their Importance

In chemistry, a buffer solution is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. These solutions are designed to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. Buffer solutions play a crucial role in various biological, medical, and industrial applications, as they help maintain a stable pH, which is essential for many chemical reactions and processes.
The effectiveness of a buffer solution depends on several factors, including the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, the dissociation constant of the acid, and the volume of the solution. In this article, we will explore the different types of buffer solutions, their working mechanisms, and which pairs work best in various situations.
How Buffer Solutions Work

A buffer solution works by neutralizing small amounts of acid or base that are added to the solution. When an acid is added, the conjugate base in the buffer solution reacts with the hydrogen ions (H+) to form the weak acid. Conversely, when a base is added, the weak acid in the buffer solution reacts with the hydroxide ions (OH-) to form the conjugate base. This reaction helps to maintain a stable pH, as the concentration of hydrogen ions remains relatively constant.
The buffering capacity of a solution is determined by the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base. A higher concentration of the conjugate base relative to the acid results in a more effective buffer solution. Additionally, the dissociation constant of the acid (Ka) plays a crucial role in determining the buffering capacity of the solution. A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, which results in a more effective buffer solution.
Types of Buffer Solutions
There are several types of buffer solutions, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of buffer solutions include:
- Phosphate buffer: A mixture of sodium phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate, commonly used in biological and medical applications.
- Tris buffer: A mixture of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and hydrochloric acid, commonly used in biochemical and molecular biology applications.
- Citrate buffer: A mixture of citric acid and sodium citrate, commonly used in food and pharmaceutical applications.
Which Pair Works Best?

The choice of buffer solution pair depends on the specific application and the desired pH range. Here are some common buffer solution pairs and their characteristics:
- Phosphate buffer pair: Sodium phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate are commonly used in biological and medical applications, such as protein purification and cell culture. This pair is effective at pH 7.0-8.0.
- Tris buffer pair: Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and hydrochloric acid are commonly used in biochemical and molecular biology applications, such as DNA and RNA extraction. This pair is effective at pH 7.0-9.0.
- Citrate buffer pair: Citric acid and sodium citrate are commonly used in food and pharmaceutical applications, such as food processing and tablet formulation. This pair is effective at pH 3.0-6.0.
When choosing a buffer solution pair, consider the following factors:
- Desired pH range: Choose a pair that is effective at the desired pH range for your application.
- Concentration: Choose a pair with the desired concentration of acid and conjugate base.
- Solubility: Choose a pair with high solubility to ensure effective buffering.
- Chemical compatibility: Choose a pair that is compatible with the chemicals and materials used in your application.
Preparation of Buffer Solutions
Preparing a buffer solution requires careful consideration of the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base. Here are the general steps to prepare a buffer solution:
- Calculate the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base required for the desired pH range.
- Weigh the acid and its conjugate base accurately using a balance.
- Dissolve the acid and its conjugate base in a solvent, such as water or buffer solution.
- Adjust the pH of the solution using a pH meter and acid or base.
- Verify the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base using a spectrophotometer or other analytical technique.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Buffer Solution Pair

In conclusion, choosing the right buffer solution pair is crucial for maintaining a stable pH in various biological, medical, and industrial applications. By understanding the working mechanisms of buffer solutions and considering factors such as pH range, concentration, and chemical compatibility, you can select the most effective buffer solution pair for your specific needs.
What do you think? Share your experiences with buffer solutions and which pairs work best for your applications.
FAQ Section:
What is the purpose of a buffer solution?
+A buffer solution is designed to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
What are the different types of buffer solutions?
+There are several types of buffer solutions, including phosphate buffer, Tris buffer, and citrate buffer.
How do I prepare a buffer solution?
+To prepare a buffer solution, calculate the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base required for the desired pH range, weigh the acid and its conjugate base accurately, dissolve the acid and its conjugate base in a solvent, adjust the pH of the solution using a pH meter and acid or base, and verify the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base using a spectrophotometer or other analytical technique.