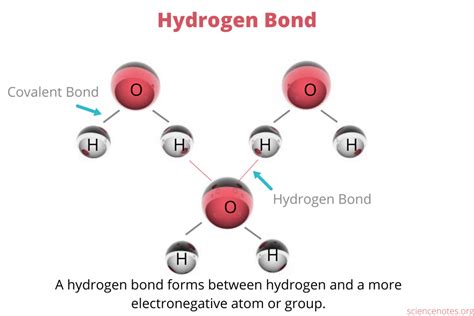
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of various biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, and water. These weak electrostatic attractions occur between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, and another electronegative atom. In this article, we will explore five compounds that can form hydrogen bonds, highlighting their importance in various biological processes.
Understanding Hydrogen Bonds

Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that arises from the difference in electronegativity between atoms. When a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom, the electrons in the bond are not shared equally. This creates a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom, which is then attracted to another electronegative atom. Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds but play a crucial role in the structure and function of biological molecules.
Characteristics of Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds have several characteristics that make them unique:
- They are relatively weak, with energies ranging from 1-30 kJ/mol.
- They are highly dependent on the distance between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom.
- They are highly directional, with the hydrogen atom forming a linear bond with the electronegative atom.
- They are highly dependent on the electronegativity of the atoms involved.
Compound 1: Water (H2O)

Water is one of the most abundant compounds in living organisms, and its ability to form hydrogen bonds is crucial for its biological functions. In water, the oxygen atom is highly electronegative, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms. This allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other, resulting in a highly cohesive liquid. Hydrogen bonds in water are responsible for its high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Water
Hydrogen bonds in water play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Protein folding and stability
- DNA replication and transcription
- Cell signaling and communication
- Temperature regulation
Compound 2: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)

DNA is a long, double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic instructions for all living organisms. Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA, particularly in the formation of the double helix. In DNA, hydrogen bonds form between the bases of the two strands, holding them together in a complementary manner. The four bases in DNA - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) - form specific hydrogen bonds with each other, allowing the DNA molecule to replicate and transmit genetic information.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in DNA
Hydrogen bonds in DNA play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- DNA replication and transcription
- Gene expression and regulation
- Mutation and evolution
- Genetic inheritance
Compound 3: Proteins (Peptides)

Proteins are complex molecules composed of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins, particularly in the formation of alpha helices and beta sheets. In proteins, hydrogen bonds form between the amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent amino acids, holding the polypeptide chain together in a specific conformation. This allows proteins to perform a wide range of biological functions, including catalysis, transport, and signaling.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Proteins
Hydrogen bonds in proteins play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Enzyme catalysis and regulation
- Cell signaling and communication
- Protein folding and stability
- Immune response and defense
Compound 4: Carbohydrates (Sugars)

Carbohydrates are a class of biomolecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of carbohydrates, particularly in the formation of glycosidic bonds. In carbohydrates, hydrogen bonds form between the hydroxyl groups of adjacent sugar molecules, holding them together in a specific conformation. This allows carbohydrates to perform a wide range of biological functions, including energy storage, cell signaling, and structural support.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Carbohydrates
Hydrogen bonds in carbohydrates play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Energy storage and metabolism
- Cell signaling and communication
- Structural support and cell wall formation
- Immune response and defense
Compound 5: Nucleotides (Nucleic acids)

Nucleotides are a class of biomolecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and one or more phosphate groups. Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of nucleotides, particularly in the formation of phosphodiester bonds. In nucleotides, hydrogen bonds form between the phosphate groups of adjacent nucleotides, holding them together in a specific conformation. This allows nucleotides to perform a wide range of biological functions, including energy transfer, cell signaling, and DNA replication.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Nucleotides
Hydrogen bonds in nucleotides play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
- Energy transfer and metabolism
- Cell signaling and communication
- DNA replication and transcription
- Gene expression and regulation
In conclusion, hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of various biological molecules, including water, DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleotides. These weak electrostatic attractions are responsible for a wide range of biological processes, including protein folding, DNA replication, and cell signaling. Understanding the importance of hydrogen bonds in these compounds can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying various biological processes.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of hydrogen bonds in various biological compounds. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Share this article with your friends and colleagues to help them understand the fascinating world of hydrogen bonds!
What is a hydrogen bond?
+A hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force that arises from the difference in electronegativity between atoms. It is a weak electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Why are hydrogen bonds important in biological molecules?
+Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates. They are responsible for the stability and specificity of these molecules, allowing them to perform a wide range of biological functions.
What are some examples of compounds that form hydrogen bonds?
+Some examples of compounds that form hydrogen bonds include water, DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleotides. These compounds are all crucial for various biological processes, including energy storage, cell signaling, and DNA replication.