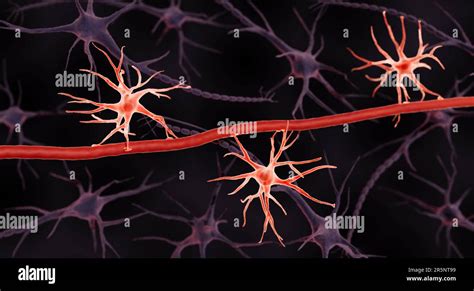
The human brain is a complex and intricate organ, comprising billions of neurons and trillions of synapses. However, the brain's complexity is not just due to its neural networks, but also due to the specialized cells that support and protect it. One such group of cells is the astrocytes, which play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's health and function. In this article, we will delve into the world of astrocytes and their relationship with the blood-brain barrier, exploring their functions, mechanisms, and importance.
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border that separates the brain from the bloodstream. It is composed of endothelial cells that line the brain's blood vessels, which are tightly packed together to form a barrier that restricts the passage of substances into the brain. The BBB is essential for maintaining the brain's homeostasis and preventing the entry of harmful substances, such as toxins and pathogens.
Astrocytes are a type of glial cell that are found throughout the brain and spinal cord. They are named for their star-shaped appearance, with long, thin processes that extend from the cell body. Astrocytes are the most numerous type of glial cell, making up approximately 20-30% of the brain's cells.
The Role of Astrocytes in the Blood-Brain Barrier

Astrocytes play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the BBB. They extend their processes to the blood vessels, where they form close interactions with the endothelial cells. These interactions are essential for the maintenance of the BBB's barrier function, as astrocytes help to regulate the expression of tight junction proteins and the transport of substances across the BBB.
Astrocytes also produce various factors that help to maintain the BBB's integrity, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietin-1. These factors help to regulate the growth and differentiation of endothelial cells, ensuring that the BBB remains intact.
Regulation of Ion and Water Balance
Astrocytes also play a crucial role in regulating the ion and water balance within the brain. They help to regulate the concentration of ions such as potassium, sodium, and chloride, which is essential for maintaining proper neuronal function.
Astrocytes also help to regulate the water balance within the brain, which is essential for maintaining proper neuronal function. They do this by controlling the expression of aquaporin-4, a water channel protein that helps to regulate the movement of water across cell membranes.
Maintenance of the Brain's Homeostasis

Astrocytes play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's homeostasis by regulating the concentration of neurotransmitters, hormones, and other signaling molecules. They help to regulate the expression of enzymes that break down these molecules, ensuring that their concentrations remain within a narrow range.
Astrocytes also help to regulate the brain's energy metabolism by controlling the expression of enzymes involved in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. This is essential for maintaining proper neuronal function, as neurons require a constant supply of energy to function properly.
Modulation of Immune Responses
Astrocytes also play a crucial role in modulating immune responses within the brain. They help to regulate the expression of cytokines and chemokines, which are signaling molecules that help to recruit immune cells to sites of inflammation.
Astrocytes also help to regulate the activity of immune cells, such as microglia and T cells, which are involved in the brain's immune response. This is essential for preventing excessive inflammation, which can damage the brain and disrupt its function.
Dysfunction of Astrocytes and the Blood-Brain Barrier

Dysfunction of astrocytes and the BBB has been implicated in a range of neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis. In these disorders, the BBB is often disrupted, allowing the entry of harmful substances into the brain.
Astrocytes also become dysfunctional in these disorders, leading to changes in their gene expression and function. This can lead to a range of problems, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and disruption of the brain's homeostasis.
Therapeutic Targeting of Astrocytes and the Blood-Brain Barrier
Targeting astrocytes and the BBB may provide a novel therapeutic approach for treating neurological disorders. Researchers are exploring various strategies, including the use of small molecules and biologics that target astrocytes and the BBB.
One promising approach is the use of astrocyte-targeted therapies, which aim to restore the function of astrocytes and the BBB. These therapies may involve the use of growth factors, cytokines, and other signaling molecules that help to regulate astrocyte function.
In conclusion, astrocytes and the blood-brain barrier play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's health and function. Dysfunction of these cells and the BBB has been implicated in a range of neurological disorders, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic approaches that target these cells and structures.
We hope that this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the importance of astrocytes and the blood-brain barrier. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is the main function of astrocytes in the brain?
+Astrocytes play a crucial role in maintaining the brain's homeostasis, regulating the concentration of ions and water, and modulating immune responses.
What is the blood-brain barrier and why is it important?
+The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective semipermeable border that separates the brain from the bloodstream, preventing the entry of harmful substances into the brain.
How do astrocytes contribute to the maintenance of the blood-brain barrier?
+Astrocytes help to regulate the expression of tight junction proteins and the transport of substances across the blood-brain barrier, maintaining its integrity.