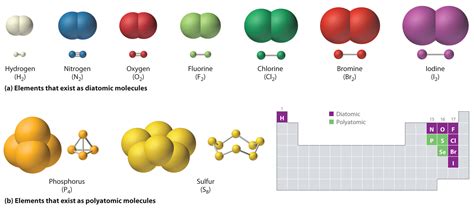
Covalent bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, where two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a molecule. This type of bonding is crucial for the formation of a wide variety of compounds, from simple molecules like water and methane to complex biomolecules like proteins and DNA. Understanding the elements that form covalent bonds is essential for grasping the principles of chemistry and the behavior of molecules.

At the heart of covalent bonding are the elements that have the ability to share electrons. These elements are typically nonmetals, which are located in the upper right corner of the periodic table. There are six key elements that are known to form covalent bonds, each with its unique properties and characteristics.
1. Hydrogen (H)
Hydrogen is the simplest element in the periodic table, with an atomic number of 1. It has one proton and one electron, which makes it an ideal candidate for forming covalent bonds. Hydrogen can form bonds with many other elements, including oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen. One of the most common compounds formed by hydrogen is water (H2O), where two hydrogen atoms share their electrons with a single oxygen atom.

Properties of Hydrogen:
- Atomic number: 1
- Atomic mass: 1.00794 u
- Electron configuration: 1s1
- Covalent radius: 37 pm
2. Carbon (C)
Carbon is a versatile element that can form covalent bonds with many other elements. It has an atomic number of 6 and an atomic mass of 12.0107 u. Carbon is a key component of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. It can form single, double, and triple bonds with other elements, which allows it to create a wide variety of compounds.

Properties of Carbon:
- Atomic number: 6
- Atomic mass: 12.0107 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p2
- Covalent radius: 67 pm
3. Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen is a vital element for life, making up about 78% of the Earth's atmosphere. It has an atomic number of 7 and an atomic mass of 14.0067 u. Nitrogen can form covalent bonds with many other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. One of the most common compounds formed by nitrogen is ammonia (NH3), where three hydrogen atoms share their electrons with a single nitrogen atom.

Properties of Nitrogen:
- Atomic number: 7
- Atomic mass: 14.0067 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p3
- Covalent radius: 71 pm
4. Oxygen (O)
Oxygen is a highly reactive element that can form covalent bonds with many other elements. It has an atomic number of 8 and an atomic mass of 15.9994 u. Oxygen is a key component of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. It can form single and double bonds with other elements, which allows it to create a wide variety of compounds.

Properties of Oxygen:
- Atomic number: 8
- Atomic mass: 15.9994 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p4
- Covalent radius: 66 pm
5. Fluorine (F)
Fluorine is a highly reactive element that can form covalent bonds with many other elements. It has an atomic number of 9 and an atomic mass of 18.9984 u. Fluorine is a key component of biomolecules, including fluorinated compounds that are used in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.

Properties of Fluorine:
- Atomic number: 9
- Atomic mass: 18.9984 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p5
- Covalent radius: 64 pm
6. Chlorine (Cl)
Chlorine is a highly reactive element that can form covalent bonds with many other elements. It has an atomic number of 17 and an atomic mass of 35.453 u. Chlorine is a key component of biomolecules, including chlorinated compounds that are used in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.

Properties of Chlorine:
- Atomic number: 17
- Atomic mass: 35.453 u
- Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
- Covalent radius: 79 pm
In conclusion, the six elements that form covalent bonds are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and chlorine. Each of these elements has unique properties and characteristics that allow them to form a wide variety of compounds. Understanding the properties and behavior of these elements is crucial for grasping the principles of chemistry and the behavior of molecules.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the six elements that form covalent bonds. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. We would love to hear from you!
What is a covalent bond?
+A covalent bond is a chemical bond that is formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Which elements form covalent bonds?
+The six elements that form covalent bonds are hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and chlorine.
What is the importance of covalent bonds in biomolecules?
+Covalent bonds play a crucial role in the formation of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids.