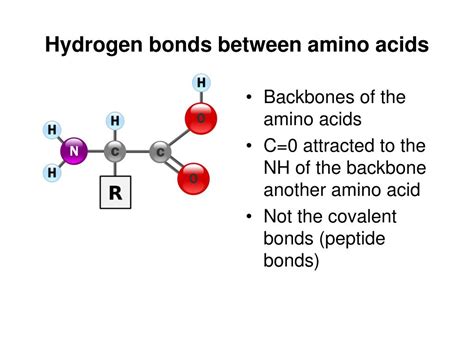
Amino Acids That Form Hydrogen Bonds

Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins. These weak electrostatic attractions between atoms help stabilize the three-dimensional conformation of proteins, allowing them to perform their biological functions. Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, are responsible for forming these hydrogen bonds. In this article, we will explore the amino acids that form hydrogen bonds and their significance in protein structure and function.
Amino acids are the fundamental components of proteins, and their unique properties enable them to interact with each other in specific ways. Hydrogen bonds are a type of non-covalent interaction that occurs between the electronegative atoms of one amino acid and the electropositive atoms of another. These bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds, but they are essential for maintaining the stability of protein structures.
The Role of Hydrogen Bonds in Protein Structure
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the formation and stabilization of protein secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. These bonds help to:
- Stabilize alpha helices and beta sheets, the fundamental elements of protein secondary structure
- Facilitate the formation of turns and loops, which are essential for protein tertiary structure
- Mediate interactions between different protein subunits, allowing them to assemble into functional complexes
Amino Acids That Form Hydrogen Bonds

Several amino acids are capable of forming hydrogen bonds, including:
- Glycine: The smallest amino acid, glycine, has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain, which can participate in hydrogen bonding.
- Serine: Serine's hydroxyl group (-OH) can act as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor.
- Threonine: Threonine's hydroxyl group (-OH) can also participate in hydrogen bonding.
- Asparagine: Asparagine's amide group (-CONH2) can act as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor.
- Glutamine: Glutamine's amide group (-CONH2) can also participate in hydrogen bonding.
- Tyrosine: Tyrosine's hydroxyl group (-OH) can act as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor.
- Histidine: Histidine's imidazole ring can participate in hydrogen bonding through its nitrogen atoms.
These amino acids can form hydrogen bonds with other amino acids, as well as with water molecules, ions, and other ligands.
The Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Protein Function
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in protein function, including:
- Enzyme-substrate interactions: Hydrogen bonds can facilitate the binding of substrates to enzymes, allowing them to perform their catalytic functions.
- Protein-ligand interactions: Hydrogen bonds can mediate the binding of ligands to proteins, enabling them to perform their biological functions.
- Protein folding: Hydrogen bonds help stabilize the native conformation of proteins, allowing them to perform their biological functions.
Factors That Influence Hydrogen Bonding in Proteins

Several factors can influence hydrogen bonding in proteins, including:
- pH: Changes in pH can affect the ionization state of amino acids, influencing their ability to form hydrogen bonds.
- Temperature: Temperature can affect the stability of hydrogen bonds, with higher temperatures often disrupting these interactions.
- Solvent: The presence of solvent molecules, such as water, can influence hydrogen bonding by competing with protein-protein interactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydrogen bonds play a vital role in protein structure and function. Amino acids such as glycine, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine, and histidine are capable of forming hydrogen bonds, which help stabilize protein secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. Understanding the factors that influence hydrogen bonding in proteins can provide valuable insights into protein function and behavior.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in protein structure?
+Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the formation and stabilization of protein secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
Which amino acids are capable of forming hydrogen bonds?
+Glycine, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine, and histidine are capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
What factors can influence hydrogen bonding in proteins?
+pH, temperature, and solvent can influence hydrogen bonding in proteins.