Understanding the Types of Ions Metals Form: An Overview

In the realm of chemistry, ions play a crucial role in understanding the properties and behavior of metals. Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Metals, being a class of elements that are typically shiny, malleable, and good conductors of electricity, can form various types of ions. In this article, we will delve into the different types of ions that metals can form and explore their characteristics.
The Formation of Cations

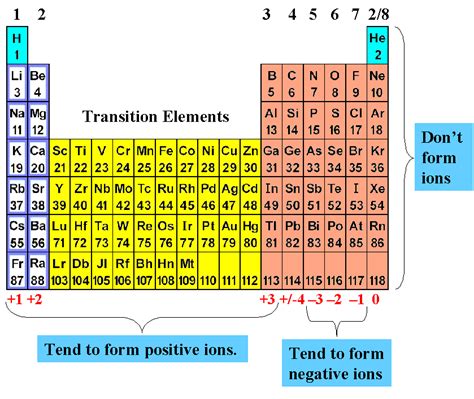
Metals tend to lose electrons to form positively charged ions, known as cations. This process occurs when a metal atom is exposed to an electric field or when it reacts with a non-metal. The number of electrons lost by the metal atom determines the charge of the resulting cation. For example, sodium (Na) loses one electron to form a +1 cation, while magnesium (Mg) loses two electrons to form a +2 cation.
Types of Cations
- Monatomic cations: These are cations composed of a single metal atom. Examples include Na+ (sodium ion) and Ca2+ (calcium ion).
- Polyatomic cations: These are cations composed of multiple metal atoms. An example is the ammonium ion (NH4+), which consists of one nitrogen atom and four hydrogen atoms.
The Formation of Anions

While metals typically form cations, some metals can also form negatively charged ions, known as anions. This occurs when a metal atom gains electrons. However, this process is less common and usually requires specific conditions.
Types of Anions
- Monatomic anions: These are anions composed of a single metal atom. An example is the oxide ion (O2-), which consists of one oxygen atom.
- Polyatomic anions: These are anions composed of multiple metal atoms. An example is the carbonate ion (CO32-), which consists of one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms.
Metal Ion Types Based on Charge

Metal ions can be classified based on their charge. This classification helps in understanding the chemical properties and behavior of metals.
Types of Metal Ions Based on Charge
- Monovalent ions: These are ions with a charge of +1 or -1. Examples include Na+ (sodium ion) and Cl- (chloride ion).
- Divalent ions: These are ions with a charge of +2 or -2. Examples include Ca2+ (calcium ion) and O2- (oxide ion).
- Trivalent ions: These are ions with a charge of +3 or -3. Examples include Al3+ (aluminum ion) and PO43- (phosphate ion).
Metal Ion Types Based on Electron Configuration

Metal ions can also be classified based on their electron configuration. This classification helps in understanding the chemical properties and behavior of metals.
Types of Metal Ions Based on Electron Configuration
- s-block ions: These are ions with a full outer energy level. Examples include Na+ (sodium ion) and Ca2+ (calcium ion).
- p-block ions: These are ions with a partially filled outer energy level. Examples include Al3+ (aluminum ion) and PO43- (phosphate ion).
- d-block ions: These are ions with a partially filled d subshell. Examples include Fe2+ (iron(II) ion) and Cu2+ (copper(II) ion).
Practical Applications of Metal Ions

Metal ions have numerous practical applications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Examples of Practical Applications
- Catalysts: Metal ions can act as catalysts in chemical reactions, increasing the reaction rate and efficiency.
- Biological systems: Metal ions play crucial roles in biological systems, such as enzyme catalysis and protein structure.
- Materials science: Metal ions are used in the development of new materials, such as batteries, fuel cells, and semiconductors.
In conclusion, metal ions are a crucial aspect of chemistry, and understanding their types and characteristics is essential for understanding the properties and behavior of metals. By recognizing the different types of ions that metals can form, we can better appreciate the complexities of chemistry and the numerous practical applications of metal ions.
What are the main types of ions that metals can form?
+Metals can form cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). Cations are more common and are formed when a metal atom loses electrons. Anions are formed when a metal atom gains electrons.
How are metal ions classified based on charge?
+Metal ions can be classified as monovalent (+1 or -1), divalent (+2 or -2), and trivalent (+3 or -3) based on their charge.
What are some practical applications of metal ions?
+Metal ions have numerous practical applications in chemistry, biology, and materials science, including catalysis, enzyme catalysis, and the development of new materials.